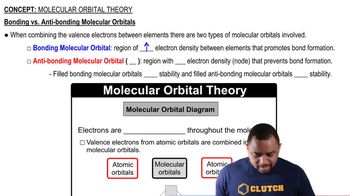
Textbook Question
According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has the highest bond order? C2, C2+ , C2- According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has the highest bond energy? According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has the shortest bond length?