Consider the reaction: C4H8( g) → 2 C2H4( g) The tabulated data were collected for the concentration of C2H4 as a function of time: a. What is the average rate of the reaction between 0 and 10 s? Between 40 and 50 s?

Consider the reaction: H2(g) + Br2(g) → 2 HBr(g) The graph shows the concentration of Br2 as a function of time.
a. Use the graph to calculate each quantity: (i) the average rate of the reaction between 0 and 25 s
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Reaction Rate
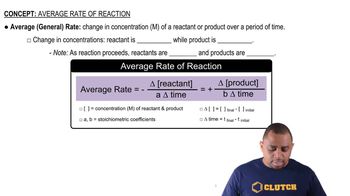
Average Rate of Reaction

Interpreting Concentration vs. Time Graphs

Consider the reaction: NO2(g) → NO(g) + 1/2 O2(g) The tabulated data were collected for the concentration of NO2 as a function of time: a. What is the average rate of the reaction between 10 and 20 s? Between 50 and 60 s?
Consider the reaction: NO2(g) → NO(g) + 1/2 O2( g) The tabulated data were collected for the concentration of NO2 as a function of time: b. What is the rate of formation of O2 between 50 and 60 s?
Consider the reaction: H2(g) + Br2(g) → 2 HBr(g) The graph shows the concentration of Br2 as a function of time. a. Use the graph to calculate each quantity: (iii) the instantaneous rate of formation of HBr at 50 s
Consider the reaction: H2( g) + Br2( g) → 2 HBr( g) The graph shows the concentration of Br2 as a function of time.
b. Make a rough sketch of a curve representing the concentration of HBr as a function of time. Assume that the initial concentration of HBr is zero
