Indicate whether each of the following statements is true or false. For each statement that is false, correct the statement to make it true. (a) Acid strength in a series of H¬A molecules increases with increasing size of A. (b) For acids of the same general structure but differing electronegativities of the central atoms, acid strength decreases with increasing electronegativity of the central atom. (c) The strongest acid known is HF because fluorine is the most electronegative element.
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 16, Problem 95
Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base among the reactants in each of the following reactions:
(a) Fe(ClO4)3(s) + 6 H2O(l) ⇌ [Fe(H2O)6]3+(aq) + 3 ClO4-(aq)
(b) CN-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ HCN(aq) + OH-(aq)
(c) (CH3)3N(g) + BF3(g) ⇌ (CH3)NBF3(s)
(d) HIO(lq) + NH2-(lq) ⇌ NH3(lq) + IO-(lq) (lq denotes liquid ammonia as solvent)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base by understanding their definitions: A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor, and a Lewis base is an electron pair donor.
Examine the reactants: HIO and NH2-. Consider which species can donate an electron pair and which can accept an electron pair.
Recognize that NH2- has a lone pair of electrons that it can donate, making it a potential Lewis base.
Consider HIO, which can accept an electron pair to form a bond, making it a potential Lewis acid.
Conclude that in the reaction, NH2- acts as the Lewis base (electron pair donor) and HIO acts as the Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor).

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Acids and Bases
Lewis acids are substances that can accept an electron pair, while Lewis bases are those that can donate an electron pair. This definition expands the concept of acids and bases beyond protons (H+) to include electron pair interactions, making it applicable to a wider range of chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
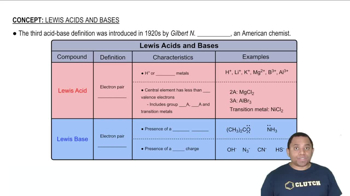
Lewis Acids and Bases
Electron Pair Donation and Acceptance
In a Lewis acid-base reaction, the Lewis base donates an electron pair to the Lewis acid, forming a coordinate covalent bond. Understanding this interaction is crucial for identifying which reactant acts as the acid and which as the base in a given reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course
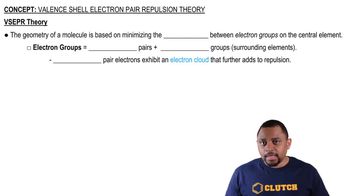
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
Solvent Effects
The solvent can influence the behavior of acids and bases in a reaction. In this case, liquid ammonia serves as a solvent, which can stabilize certain ions and affect the reactivity of the reactants, thereby impacting the identification of Lewis acids and bases in the reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Photoelectric Effect
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The fluoride ion reacts with water to produce HF. (c) Is fluoride acting as a Lewis acid or as a Lewis base when reacting with water?
Textbook Question
Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base in each of the following reactions:
(a) HNO2(aq) + OH-(aq) ⇌ NO2-(aq) + H2O(l)
(b) FeBr3(s) + Br-(aq) ⇌ FeBr4-(aq)
(c) Zn2+(aq) + 4 NH3(aq) ⇌ Zn(NH3)42+(aq)
(d) SO2(g) + H2O(l) ⇌ H2SO3(aq)
Textbook Question
Which member of each pair produces the more acidic aqueous solution: (a) ZnBr2 or CdCl2 (b) CuCl or Cu(NO3)2 (c) Ca(NO3)2 or NiBr2
