Ch.22 - The Main Group Elements

Chapter 22, Problem 105a
Identify the group 5A element that best fits each of the following descriptions.
(a) Forms strong π bonds
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the elements in group 5A (also known as group 15) of the periodic table. These elements are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), and bismuth (Bi).
Understand that strong π bonds are typically formed by elements that can effectively overlap their p orbitals.
Consider the size of the atoms: smaller atoms can form stronger π bonds because their p orbitals can overlap more effectively.
Recognize that nitrogen, being the smallest atom in group 5A, is most capable of forming strong π bonds due to its small size and ability to effectively overlap its p orbitals.
Conclude that nitrogen is the group 5A element that best fits the description of forming strong π bonds.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Group 5A Elements
Group 5A elements, also known as Group 15 in the periodic table, include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), and bismuth (Bi). These elements have five valence electrons, which allows them to form various types of bonds, including covalent bonds with other nonmetals. Understanding their bonding behavior is crucial for identifying which element fits specific descriptions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
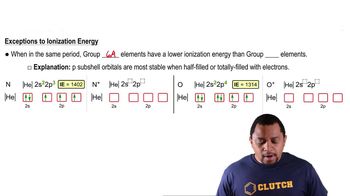
Group 6A vs. Group 5A Elements
π Bonds
π bonds are a type of covalent bond that occurs when two lobes of an orbital on one atom overlap with two lobes of an orbital on another atom, forming a bond above and below the axis connecting the two nuclei. They are typically found in double and triple bonds, where they accompany σ bonds. The ability of an element to form strong π bonds is often associated with its electronegativity and the availability of p orbitals.
Recommended video:
Guided course
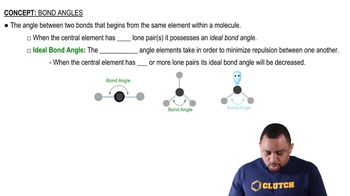
Bond Angles
Electronegativity and Bonding
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold onto electrons in a bond. In the context of Group 5A elements, nitrogen is the most electronegative, which contributes to its ability to form strong π bonds, particularly in compounds like nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3). Understanding electronegativity helps in predicting the strength and type of bonds that elements can form.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Electronegativity Trends
Related Practice
