Textbook Question
Which member of each pair produces the more acidic aqueous solution: (a) ZnBr2 or CdCl2 (b) CuCl or Cu(NO3)2 (c) Ca(NO3)2 or NiBr2

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
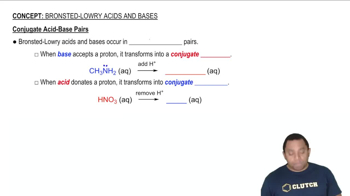

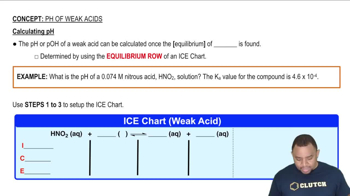
Which member of each pair produces the more acidic aqueous solution: (a) ZnBr2 or CdCl2 (b) CuCl or Cu(NO3)2 (c) Ca(NO3)2 or NiBr2
Indicate whether each of the following statements is correct or incorrect. (d) K+ ion is acidic in water because it causes hydrating water molecules to become more acidic.
A solution is made by adding 0.300 g Ca1OH221s2, 50.0 mL of 1.40 M HNO3, and enough water to make a final volume of 75.0 mL. Assuming that all of the solid dissolves, what is the pH of the final solution?