Molecular Geometry and Hybridization
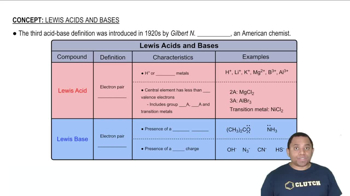
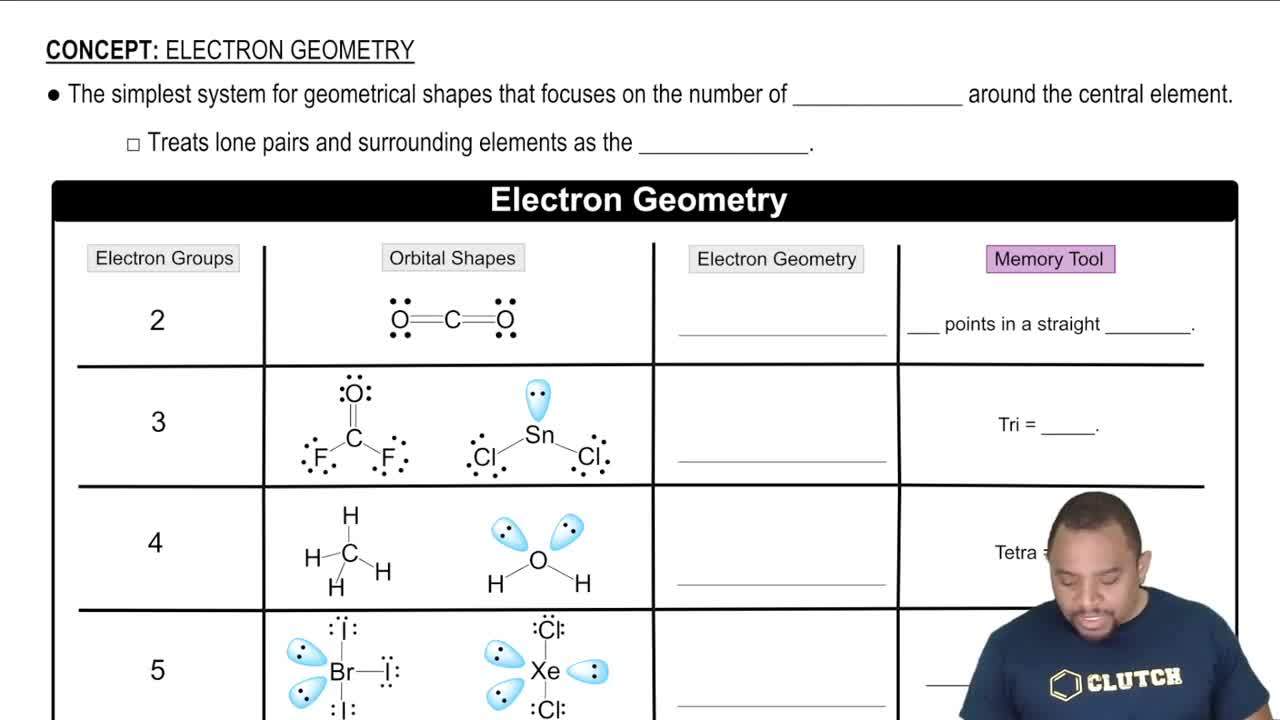
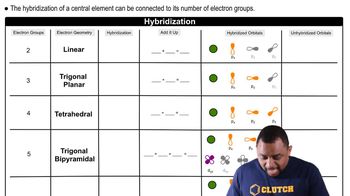
The molecular geometry and hybridization of a compound influence its reactivity and acid-base behavior. BF3 has a trigonal planar geometry with sp2 hybridization, which allows for effective orbital overlap when accepting electron pairs. In contrast, BH3, with its similar geometry, is less electron-deficient, making BF3 the stronger Lewis acid in this comparison.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance