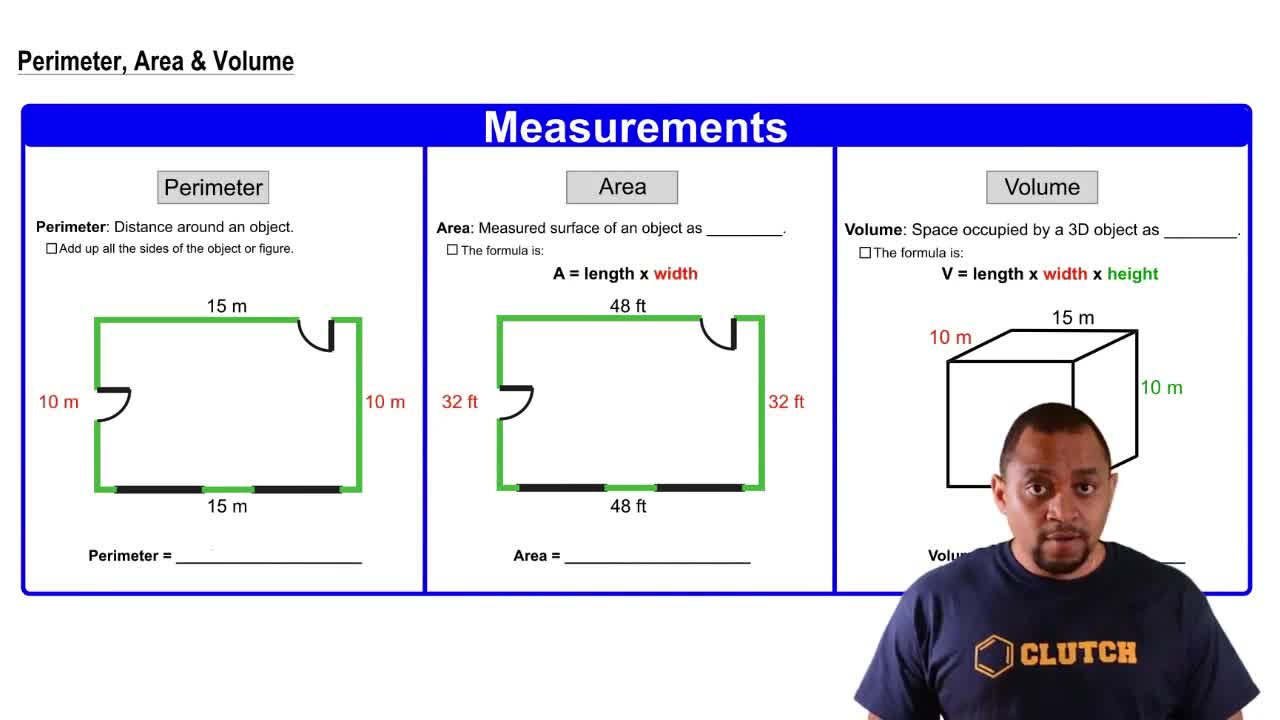
Textbook Question
The addition of NO accelerates the decomposition of N2O, possibly by the following mechanism: NO1g2 + N2O1g2¡N21g2 + NO21g2 2 NO21g2¡2 NO1g2 + O21g2 (b) Is NO serving as a catalyst or an intermediate in this reaction?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
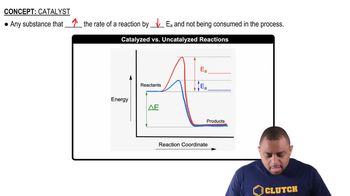
The addition of NO accelerates the decomposition of N2O, possibly by the following mechanism: NO1g2 + N2O1g2¡N21g2 + NO21g2 2 NO21g2¡2 NO1g2 + O21g2 (b) Is NO serving as a catalyst or an intermediate in this reaction?
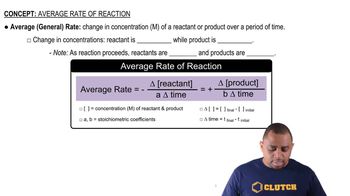
The enzyme urease catalyzes the reaction of urea, (NH2CONH2), with water to produce carbon dioxide and ammonia. In water, without the enzyme, the reaction proceeds with a first-order rate constant of 4.15 × 10-5 s-1 at 100°C. In the presence of the enzyme in water, the reaction proceeds with a rate constant of 3.4 × 104 s-1 at 21°C. (b) If the rate of the catalyzed reaction were the same at 100°C as it is at 21°C, what would be the difference in the activation energy between the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions?