Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Accounting
- 2. Transaction Analysis
- 3. Accrual Accounting Concepts
- Accrual Accounting vs. Cash Basis Accounting
- Revenue Recognition and Expense Recognition
- Introduction to Adjusting Journal Entries and Prepaid Expenses
- Adjusting Entries: Supplies
- Adjusting Entries: Unearned Revenue
- Adjusting Entries: Accrued Expenses
- Adjusting Entries: Accrued Revenues
- Adjusting Entries: Depreciation
- Summary of Adjusting Entries
- Unadjusted vs Adjusted Trial Balance
- Closing Entries
- Post-Closing Trial Balance
- 4. Merchandising Operations
- Service Company vs. Merchandising Company
- Net Sales
- Cost of Goods Sold - Perpetual Inventory vs. Periodic Inventory
- Perpetual Inventory - Purchases
- Perpetual Inventory - Freight Costs
- Perpetual Inventory - Purchase Discounts
- Perpetual Inventory - Purchasing Summary
- Periodic Inventory - Purchases
- Periodic Inventory - Freight Costs
- Periodic Inventory - Purchase Discounts
- Periodic Inventory - Purchasing Summary
- Single-step Income Statement
- Multi-step Income Statement
- Comprehensive Income
- 5. Inventory
- Merchandising Company vs. Manufacturing Company
- Physical Inventory Count, Ownership of Goods, and Consigned Goods
- Specific Identification
- Periodic Inventory - FIFO, LIFO, and Average Cost
- Perpetual Inventory - FIFO, LIFO, and Average Cost
- Financial Statement Effects of Inventory Costing Methods
- Lower of Cost or Market
- Inventory Errors
- 6. Internal Controls and Reporting Cash
- 7. Receivables and Investments
- Types of Receivables
- Net Accounts Receivable: Direct Write-off Method
- Net Accounts Receivable: Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
- Net Accounts Receivable: Percentage of Sales Method
- Net Accounts Receivable: Aging of Receivables Method
- Notes Receivable
- Introduction to Investments in Securities
- Trading Securities
- Available-for-Sale (AFS) Securities
- Held-to-Maturity (HTM) Securities
- Equity Method
- 8. Long Lived Assets
- Initial Cost of Long Lived Assets
- Basket (Lump-sum) Purchases
- Ordinary Repairs vs. Capital Improvements
- Depreciation: Straight Line
- Depreciation: Declining Balance
- Depreciation: Units-of-Activity
- Depreciation: Summary of Main Methods
- Depreciation for Partial Years
- Retirement of Plant Assets (No Proceeds)
- Sale of Plant Assets
- Change in Estimate: Depreciation
- Intangible Assets and Amortization
- Natural Resources and Depletion
- Asset Impairments
- Exchange for Similar Assets
- 9. Current Liabilities
- 10. Time Value of Money
- 11. Long Term Liabilities
- 12. Stockholders' Equity
- Characteristics of a Corporation
- Shares Authorized, Issued, and Outstanding
- Issuing Par Value Stock
- Issuing No Par Value Stock
- Issuing Common Stock for Assets or Services
- Retained Earnings
- Retained Earnings: Prior Period Adjustments
- Preferred Stock
- Treasury Stock
- Dividends and Dividend Preferences
- Stock Dividends
- Stock Splits
- 13. Statement of Cash Flows
- 14. Financial Statement Analysis
- Horizontal Analysis
- Vertical Analysis
- Common-sized Statements
- Trend Percentages
- Discontinued Operations and Extraordinary Items
- Introduction to Ratios
- Ratios: Earnings Per Share (EPS)
- Ratios: Working Capital and the Current Ratio
- Ratios: Quick (Acid Test) Ratio
- Ratios: Gross Profit Rate
- Ratios: Profit Margin
- Ratios: Quality of Earnings Ratio
- Ratios: Inventory Turnover
- Ratios: Average Days in Inventory
- Ratios: Accounts Receivable (AR) Turnover
- Ratios: Average Collection Period (Days Sales Outstanding)
- Ratios: Return on Assets (ROA)
- Ratios: Total Asset Turnover
- Ratios: Fixed Asset Turnover
- Ratios: Profit Margin x Asset Turnover = Return On Assets
- Ratios: Accounts Payable Turnover
- Ratios: Days Payable Outstanding (DPO)
- Ratios: Times Interest Earned (TIE)
- Ratios: Debt to Asset Ratio
- Ratios: Debt to Equity Ratio
- Ratios: Payout Ratio
- Ratios: Dividend Yield Ratio
- Ratios: Return on Equity (ROE)
- Ratios: DuPont Model for Return on Equity (ROE)
- Ratios: Free Cash Flow
- Ratios: Price-Earnings Ratio (PE Ratio)
- Ratios: Book Value per Share of Common Stock
- Ratios: Cash to Monthly Cash Expenses
- Ratios: Cash Return on Assets
- Ratios: Economic Return from Investing
- Ratios: Capital Acquisition Ratio
- 15. GAAP vs IFRS
- GAAP vs. IFRS: Introduction
- GAAP vs. IFRS: Classified Balance Sheet
- GAAP vs. IFRS: Recording Differences
- GAAP vs. IFRS: Adjusting Entries
- GAAP vs. IFRS: Merchandising
- GAAP vs. IFRS: Inventory
- GAAP vs. IFRS: Fraud, Internal Controls, and Cash
- GAAP vs. IFRS: Receivables
- GAAP vs. IFRS: Long Lived Assets
- GAAP vs. IFRS: Liabilities
- GAAP vs. IFRS: Stockholders' Equity
- GAAP vs. IFRS: Statement of Cash Flows
- GAAP vs. IFRS: Analysis and Income Statement Presentation
12. Stockholders' Equity
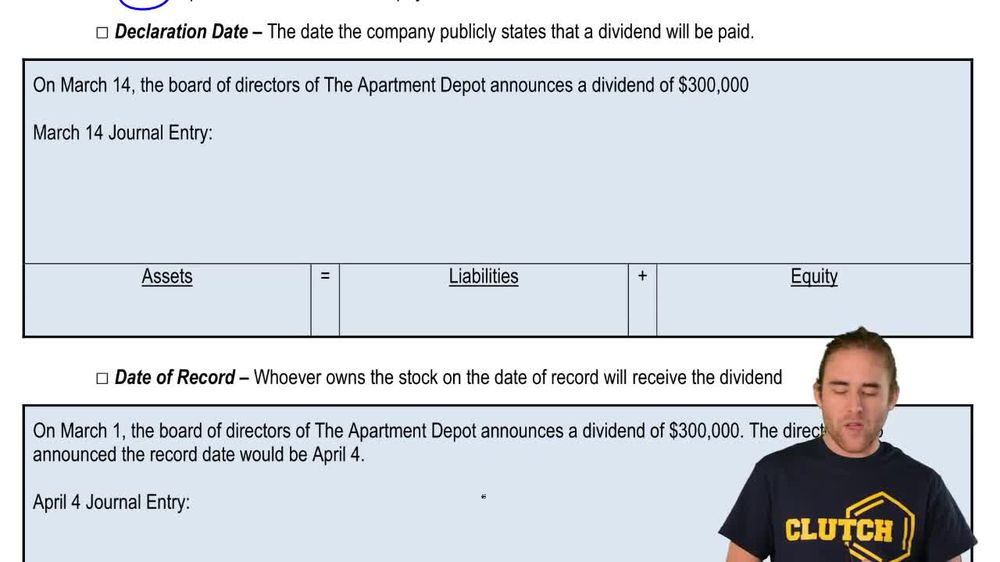
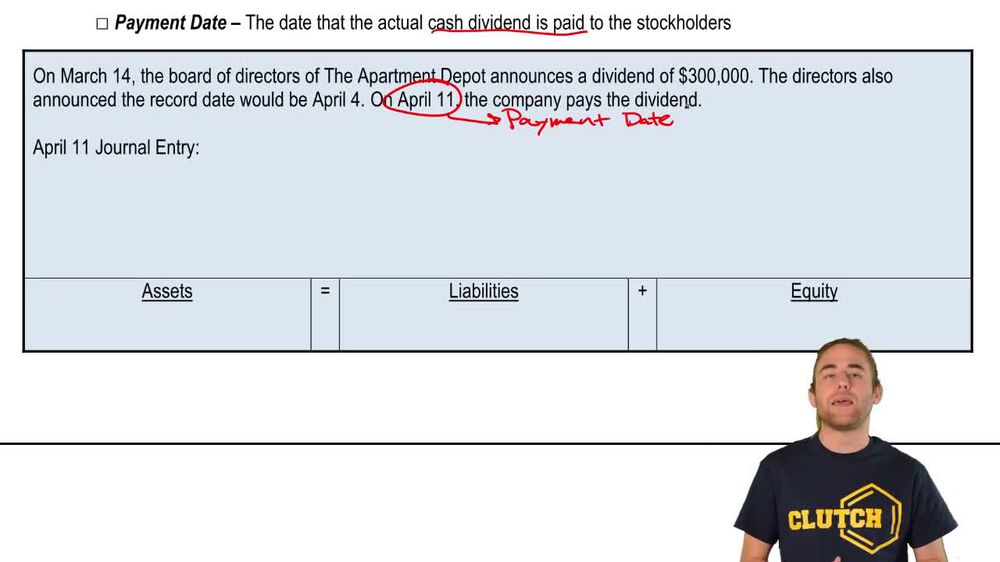
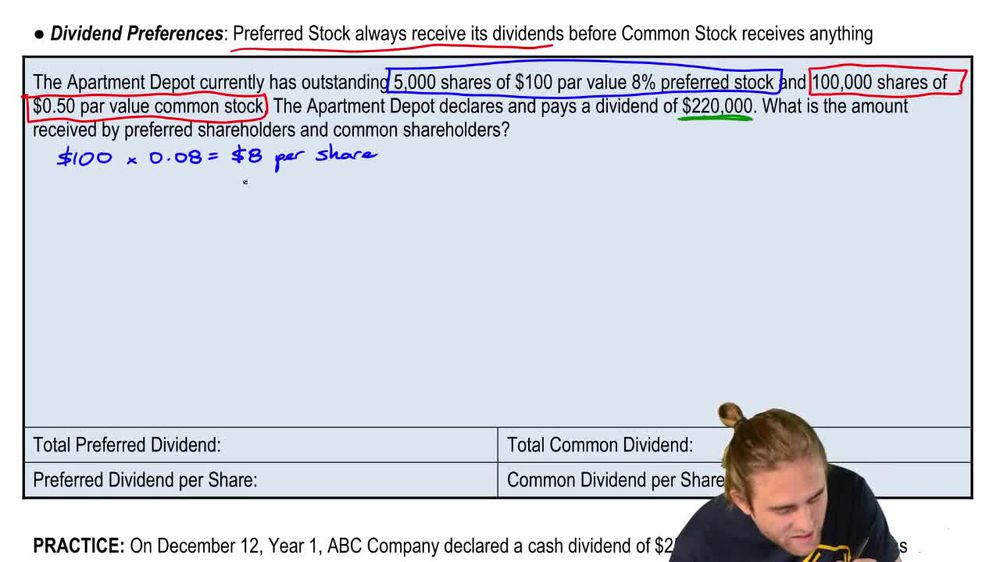
Dividends and Dividend Preferences
12. Stockholders' Equity
Dividends and Dividend Preferences
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
On December 12, Year 1, ABC Company declared a cash dividend of \$250,000. The date of record was December 28, Year 1. The cash dividend was paid on January 5, Year 2. During which period will the dividend be included on the Statement of Retained Earnings?
- Multiple Choice
ABC Company declared and paid a dividend of \$150,000 during the current year. The amount of common stock (\$0.50 par value) outstanding was 125,000. The amount of \$6 preferred shares (par value of \$100) outstanding was 1,000. What is the total dividend received by common stockholders?