Back
BackProblem 61
Let ƒ(x)=2x-3 and g(x)=-x+3. Find each function value. (g∘ƒ)(0)
Problem 62
Let ƒ(x)=-3x+4 and g(x)=-x2+4x+1. Find each of the following. Simplify if necessary. g(-x)
Problem 62
For each line described, write an equation in
(a)slope-intercept form, if possible, and
(b)standard form.
through and
Problem 62
Determine whether each function is even, odd, or neither. ƒ(x)=x4-5x+8
Problem 63
Let ƒ(x)=-3x+4 and g(x)=-x2+4x+1. Find each of the following. Simplify if necessary. ƒ(x+2)
Problem 63
Let ƒ(x)=2x-3 and g(x)=-x+3. Find each function value. See Example 5.
Problem 63
Determine whether each function is even, odd, or neither. ƒ(x)=x+1/x5
Problem 63
Graph the line passing through the given point and having the indicated slope. Plot two points on the line. through (- 5/2 , 3), undefined slope
Problem 64
For each line described, write an equation in (a) slope-intercept form, if possible, and (b) standard form. x - intercept (-3, 0), y-intercept (0, 5)
Problem 64
Let ƒ(x)=2x-3 and g(x)=-x+3. Find each function value. See Example 5.
Problem 64
Graph the line passing through the given point and having the indicated slope. Plot two points on the line. through (9/4 , 2), undefined slope
Problem 64
Determine whether each function is even, odd, or neither. ƒ(x)=x4+4/x2
Problem 64
Let ƒ(x)=-3x+4 and g(x)=-x2+4x+1. Find each of the following. Simplify if necessary. ƒ(a+4)
Problem 65
For each line described, write an equation in
(a)slope-intercept form, if possible, and
(b)standard form.
through , perpendicular to a line with undefined slope.
Problem 65
Let ƒ(x)=-3x+4 and g(x)=-x2+4x+1. Find each of the following. Simplify if necessary. ƒ(2m-3)
Problem 66
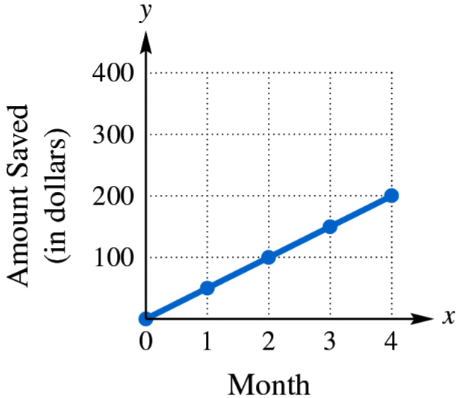
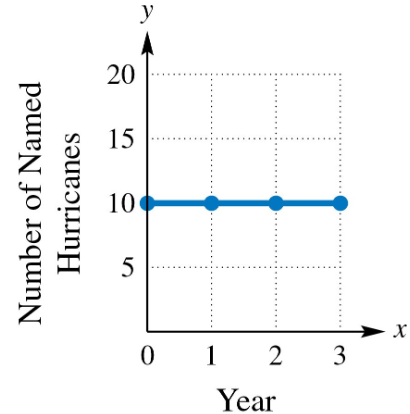
Find and interpret the average rate of change illustrated in each graph.
Problem 66
For each line described, write an equation in
(a)slope-intercept form, if possible, and
(b)standard form.
through , perpendicular to
Problem 66
Let ƒ(x)=-3x+4 and g(x)=-x2+4x+1. Find each of the following. Simplify if necessary. ƒ(3t-2)
Problem 67
For each line described, write an equation in (a) slope-intercept form, if possible, and (b) standard form. through (-7, 4), perpendicular to y = 8
Problem 67
Graph each function. See Examples 6–8 and the Summary of Graphing Techniques box following Example 9. ƒ(x)=x2+2
Problem 67
For each function, find (a) ƒ(2) and (b) ƒ(-1). ƒ = {(-1,3),(4,7),(0,6),(2,2)}
Problem 68
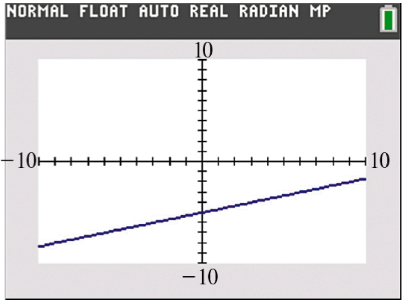
Solve each problem. A graph of y=ƒ(x) is shown in the standard viewing window. Which is the only value of x that could possibly be the solution of the equation ƒ(x) =0? A. -15 B. 0 C. 5 D. 15
Problem 68
For each line described, write an equation in (a) slope-intercept form, if possible, and (b) standard form. through (3, -5), parallel to y = 4
Problem 68
For each function, find (a) ƒ(2) and (b) ƒ(-1).See Example 7. ƒ = {(2,5),(3,9),(-1,11),(5,3)}
Problem 68
Find and interpret the average rate of change illustrated in each graph.
Problem 69
Graph each function.
Problem 70
Graph each function.
Problem 70
Use a graphing calculator to solve each linear equation. 7x-2x+ 4-5=3x+1
Problem 71
Graph each function. See Examples 6–8 and the Summary of Graphing Techniques box following Example 9. g(x)=(x+2)2
Problem 71
Use a graphing calculator to solve each linear equation. 3(2x+1) - 2 (x-2) =5