Back
BackProblem 39a
In Exercises 35–46, determine the constant that should be added to the binomial so that it becomes a perfect square trinomial. Then write and factor the trinomial. x2 + 3x
Problem 40a
Exercises 27–40 contain linear equations with constants in denominators. Solve each equation. 3x/5 - (x - 3)/2 = (x + 2)/3
Problem 41
In all exercises, other than exercises with no solution, use interval notation to express solution sets and graph each solution set on a number line. In Exercises 27–50, solve each linear inequality. x/4 - 3/2 ≤ x/2 + 1
Problem 41
In Exercises 37–52, perform the indicated operations and write the result in standard form. (- 2 + √-4)2
Problem 41
In Exercises 35–46, determine the constant that should be added to the binomial so that it becomes a perfect square trinomial. Then write and factor the trinomial.
Problem 41
In Exercises 35–54, solve each formula for the specified variable. Do you recognize the formula? If so, what does it describe? E = mc2 for m
Problem 41
Exercises 41–60 contain rational equations with variables in denominators. For each equation, a. write the value or values of the variable that make a denominator zero. These are the restrictions on the variable. b. Keeping the restrictions in mind, solve the equation. 4/x = 5/2x + 3
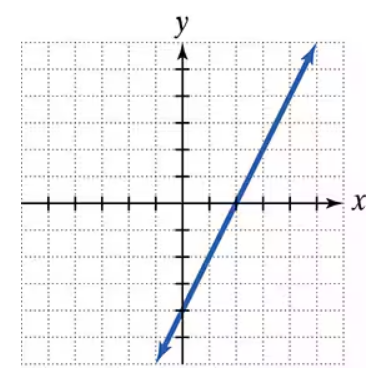
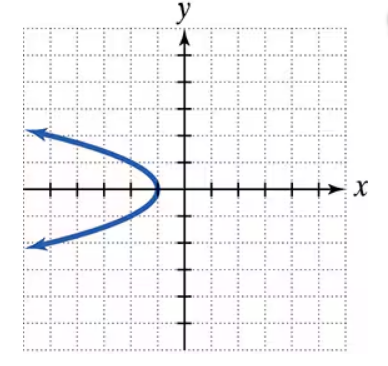
Problem 41a
Use the graph to a. determine the x-intercepts, if any; b. determine the y-intercepts, if any. For each graph, tick marks along the axes represent one unit each.
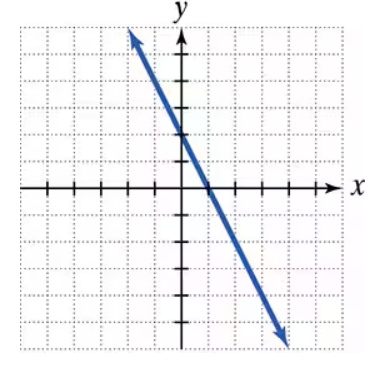
Problem 42
Use the graph to a. determine the x-intercepts, if any; b. determine the y-intercepts, if any. For each graph, tick marks along the axes represent one unit each.
Problem 43
In all exercises, other than exercises with no solution, use interval notation to express solution sets and graph each solution set on a number line. In Exercises 27–50, solve each linear inequality. 1 - x/2 > 4
Problem 43
In Exercises 35–46, determine the constant that should be added to the binomial so that it becomes a perfect square trinomial. Then write and factor the trinomial.
Problem 43
Solve each equation in Exercises 41–60 by making an appropriate substitution.
Problem 43
In Exercises 37–52, perform the indicated operations and write the result in standard form. (- 3 - √-7)2
Problem 43
In Exercises 36–43, use the five-step strategy for solving word problems. The length of a rectangular field is 6 yards less than triple the width. If the perimeter of the field is 340 yards, what are its dimensions?
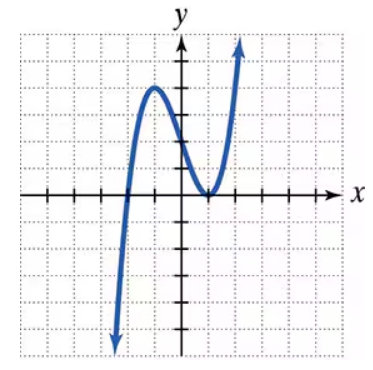
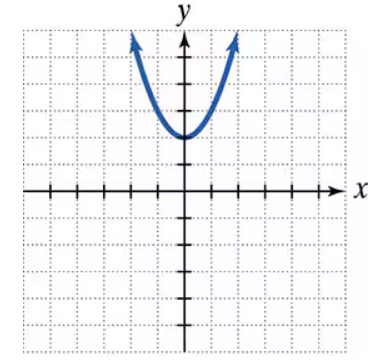
Problem 43a
Use the graph to a. determine the x-intercepts, if any; b. determine the y-intercepts, if any. For each graph, tick marks along the axes represent one unit each.
- Solve and check: 24 + 3 (x + 2) = 5(x − 12).
Problem 44
Problem 44
Exercises 41–60 contain rational equations with variables in denominators. For each equation, a. write the value or values of the variable that make a denominator zero. These are the restrictions on the variable. b. Keeping the restrictions in mind, solve the equation. 7/2x - 5/3x = 22/3
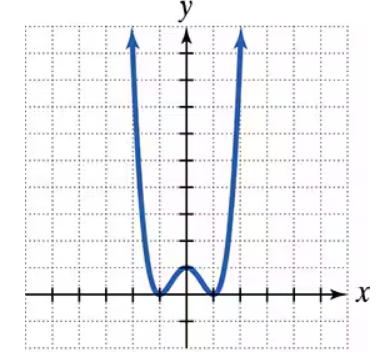
Problem 44a
Use the graph to a. determine the x-intercepts, if any; b. determine the y-intercepts, if any. For each graph, tick marks along the axes represent one unit each.
Problem 45
Solve each equation in Exercises 41–60 by making an appropriate substitution. x - 13√x + 40 = 0
Problem 45
In all exercises, other than exercises with no solution, use interval notation to express solution sets and graph each solution set on a number line. In Exercises 27–50, solve each linear inequality. (x - 4)/6 ≥ (x - 2)/9 + 5/18
Problem 45
In Exercises 37–52, perform the indicated operations and write the result in standard form. (- 8 + √-32)/24
Problem 45
In Exercises 35–46, determine the constant that should be added to the binomial so that it becomes a perfect square trinomial. Then write and factor the trinomial.
Problem 45
In Exercises 45–47, solve each formula for the specified variable. vt + gt^2 = s for g
Problem 45a
Use the graph to a. determine the x-intercepts, if any; b. determine the y-intercepts, if any. For each graph, tick marks along the axes represent one unit each.
Problem 46
Exercises 41–60 contain rational equations with variables in denominators. For each equation, a. write the value or values of the variable that make a denominator zero. These are the restrictions on the variable. b. Keeping the restrictions in mind, solve the equation. 5/2x - 8/9 = 1/18 - 1/3x
Problem 46a
Use the graph to a. determine the x-intercepts, if any; b. determine the y-intercepts, if any. For each graph, tick marks along the axes represent one unit each.
Problem 47
In Exercises 45–47, solve each formula for the specified variable. T = (A-P)/Pr for P
Problem 47
In all exercises, other than exercises with no solution, use interval notation to express solution sets and graph each solution set on a number line. In Exercises 27–50, solve each linear inequality. 4(3x - 2) - 3x < 3(1 + 3x) - 7
Problem 47
In Exercises 35–54, solve each formula for the specified variable. Do you recognize the formula? If so, what does it describe? S = P + Prt for r
Problem 47
Perform the indicated operations and write the result in standard form.