Indicate what is correct and incorrect about this statement: If lizards want to survive during climate change, they can evolve new life-history traits.

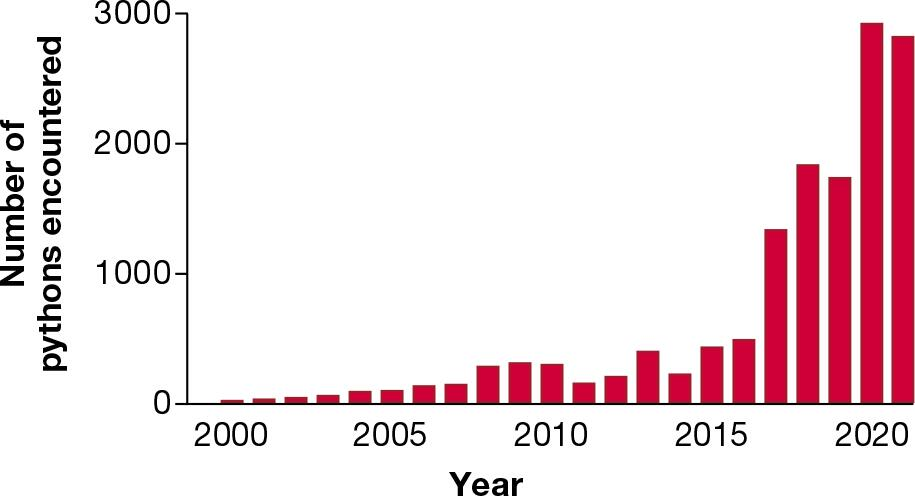
Burmese pythons (Python molurus bivittatus) are constricting snakes that can reach enormous sizes (up to 7 meters in length). They are native to Southeast Asia but were released into southern Florida from the pet trade. Many other snakes occur naturally in this area. Are the introduced pythons a problem? Burmese pythons were first found in the wetlands of Everglades National Park in the 1980s, but only rarely. The accompanying graph shows what happened next. Most of the data are derived from chance encounters of pythons on roads and intermittent search effort near roads (pythons are notoriously difficult to find). Despite the variability in search effort, what type of population growth best describes the trend in the data from 2000 to 2020? a. logistic b. exponential c. linear d. logarithmic
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Population Growth Models
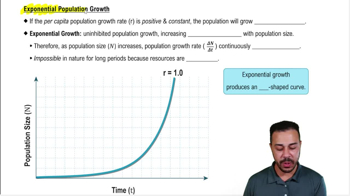
Exponential Growth
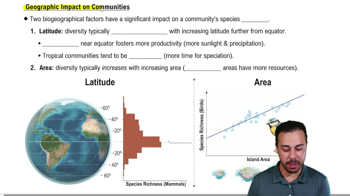
Invasive Species Impact
When wild plant and animal populations are logged, fished, or hunted, only the oldest or largest individuals tend to be taken. Many of the commercially important species are long lived and are slow to begin reproducing. If harvesting is not regulated carefully and exploitation is intense, what impact does harvesting have on a population's age structure? How might harvesting affect the population's life table and growth rate?
<Image>
Burmese pythons (Python molurus bivittatus) are constricting snakes that can reach enormous sizes (up to 7 meters in length). They are native to Southeast Asia but were released into southern Florida from the pet trade. Many other snakes occur naturally in this area. Are the introduced pythons a problem?
Researchers hypothesize that the severe winter of 2010 caused the decline in the number of pythons encountered that year. Is cold weather typically a density-dependent factor or a density-independent factor? Explain the difference.
<Image>
Burmese pythons (Python molurus bivittatus) are constricting snakes that can reach enormous sizes (up to 7 meters in length). They are native to Southeast Asia but were released into southern Florida from the pet trade. Many other snakes occur naturally in this area. Are the introduced pythons a problem?
The data in the graph show the number of pythons that were encountered, not the total number of pythons in the population. Design a mark–recapture experiment to estimate the total population size of pythons, and list at least two assumptions you would be making in your experiment.
<Image>
Burmese pythons (Python molurus bivittatus) are constricting snakes that can reach enormous sizes (up to 7 meters in length). They are native to Southeast Asia but were released into southern Florida from the pet trade. Many other snakes occur naturally in this area. Are the introduced pythons a problem?
A life table would help researchers make predictions about python population growth. If you were to track a cohort of pythons over time to construct a detailed life table, what kind of data would you want to collect?
