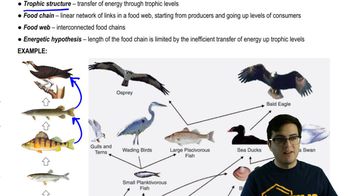
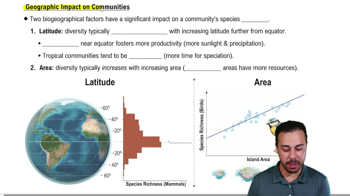
<Image>
Burmese pythons (Python molurus bivittatus) are constricting snakes that can reach enormous sizes (up to 7 meters in length). They are native to Southeast Asia but were released into southern Florida from the pet trade. Many other snakes occur naturally in this area. Are the introduced pythons a problem?
Researchers hypothesize that the severe winter of 2010 caused the decline in the number of pythons encountered that year. Is cold weather typically a density-dependent factor or a density-independent factor? Explain the difference.