Ch. 48 - The Immune System in Animals

Chapter 48, Problem 15
Lipid nanoparticle formulations of self-amplifying RNA contain lipids, phospholipids, and cholesterol (for review, see Ch. 7, Section 7.5). By which process do they enter cells?
a. beating cilia
b. phagocytosis
c. receptor-mediated endocytosis
d. macropinocytosis
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the components of the lipid nanoparticle formulations mentioned in the question: lipids, phospholipids, and cholesterol.
Understand the nature of lipid nanoparticles and their interaction with cell membranes, which are also composed of lipid bilayers.
Review the listed cellular processes to determine which is most likely involved in the internalization of lipid-based particles. The processes listed are: beating cilia, phagocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and macropinocytosis.
Consider the specificity and mechanism of receptor-mediated endocytosis, which involves the cell surface receptors binding to specific molecules (ligands), leading to the formation of vesicles that internalize the ligand-receptor complexes.
Evaluate how the lipid composition of the nanoparticles might interact with cell membrane receptors to facilitate entry into cells via receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lipid Nanoparticles
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are small lipid-based carriers that encapsulate nucleic acids, such as RNA, to facilitate their delivery into cells. They are composed of lipids, phospholipids, and cholesterol, which help stabilize the RNA and enhance cellular uptake. LNPs are particularly important in mRNA vaccine technology, as they protect the RNA from degradation and promote efficient delivery to target cells.
Recommended video:
Guided course
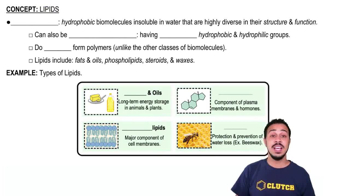
Lipids
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell by engulfing them in a membrane-bound vesicle. This process is crucial for the uptake of large molecules, such as RNA encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles. There are various forms of endocytosis, including receptor-mediated endocytosis, which is highly specific and involves the binding of ligands to cell surface receptors.
Recommended video:
Guided course
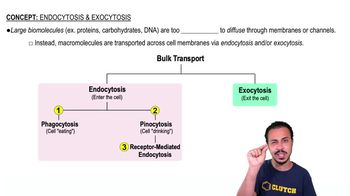
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Receptor-mediated endocytosis is a selective process where cells internalize specific molecules based on their recognition by cell surface receptors. This mechanism allows for the efficient uptake of nutrients, hormones, and other signaling molecules. In the context of lipid nanoparticles, this process enables the targeted delivery of RNA to cells, enhancing the effectiveness of therapies such as vaccines.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Endocytosis and Exocytosis Example 1
Related Practice
