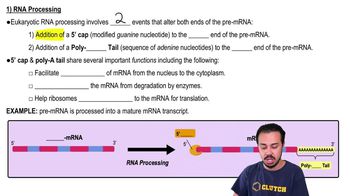
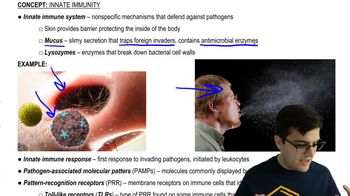
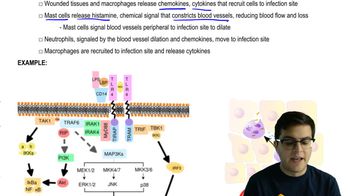
Innate Immune Response
The innate immune response is the body's first line of defense against pathogens, involving immediate, non-specific responses. This includes the activation of immune cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, which can recognize and respond to the presence of foreign RNA. The recognition of viral RNA can trigger the release of cytokines and interferons, enhancing the overall immune response and preparing the adaptive immune system for a more targeted attack.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance