Textbook Question
Calculate and compare the caloric content of skim milk and whole milk. Per serving, skim milk contains 12 g carbohydrates, 8 g protein, and no fat; whole milk contains 12 g carbohydrates, 8 g protein, and 8 g fat.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
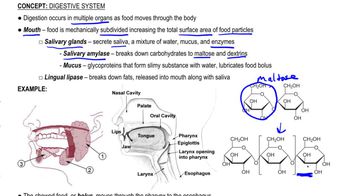
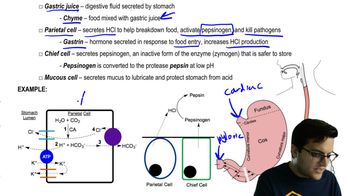
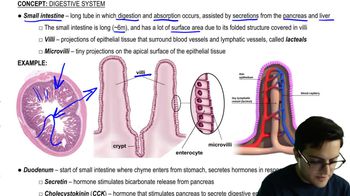
Calculate and compare the caloric content of skim milk and whole milk. Per serving, skim milk contains 12 g carbohydrates, 8 g protein, and no fat; whole milk contains 12 g carbohydrates, 8 g protein, and 8 g fat.
Cellulose is fermented in which of the following structures in rabbits?
a. Small intestine
b. Cecum
c. Abomasum
d. Rumen
A hormone that reduces the blood glucose level is______, and a hormone that increases the blood glucose level is__________.
Explain the role in nutrition of each of the following structures:
bird crop, cow rumen, and elephant cecum.