Calculate and compare the caloric content of skim milk and whole milk. Per serving, skim milk contains 12 g carbohydrates, 8 g protein, and no fat; whole milk contains 12 g carbohydrates, 8 g protein, and 8 g fat.

A hormone that reduces the blood glucose level is______, and a hormone that increases the blood glucose level is__________.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Insulin
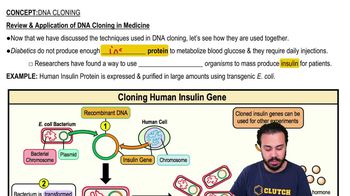
Glucagon
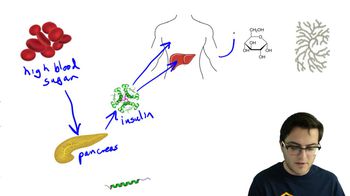
Blood Glucose Regulation

Evaluate the following statements regarding digestion; select True or False for each statement.
T/F Salivary amylase completes the digestion of starch into monosaccharides.
T/F Pepsin digests proteins in the stomach.
T/F Trypsin digests disaccharides into monosaccharides.
T/F Pancreatic lipase performs the majority of chemical digestion of lipids.
Cellulose is fermented in which of the following structures in rabbits?
a. Small intestine
b. Cecum
c. Abomasum
d. Rumen
Explain the role in nutrition of each of the following structures:
bird crop, cow rumen, and elephant cecum.
Why is oral rehydration therapy with a solution of sodium chloride and glucose an effective treatment for dehydration?
a. The sodium and glucose decrease urine output.
b. The sodium and glucose facilitate water absorption by the small intestine.
c. The sodium and glucose help kill intestinal bacteria.
d. The sodium and glucose make the person thirsty.
Why is it important that the small intestine has a much greater surface area than the stomach or esophagus?
