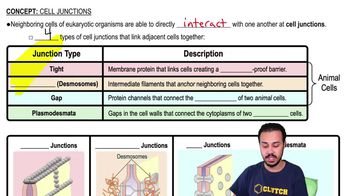
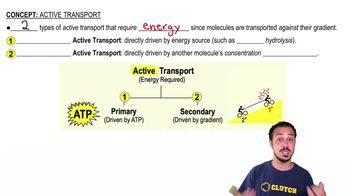
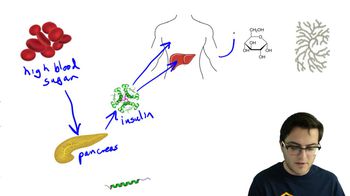
A cell is placed in a solution that is hypotonic to the cell. Which of the following best describes movement of water in this situation?
a. Water will only flow into the cell.
b. Water will only flow out of the cell.
c. Water will flow into and out of the cell, but the overall net movement will be out of the cell.
d. Water will flow into and out of the cell, but the overall net movement will be into the cell.