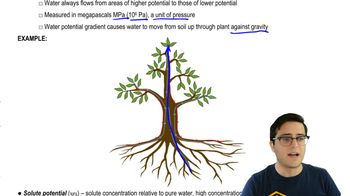
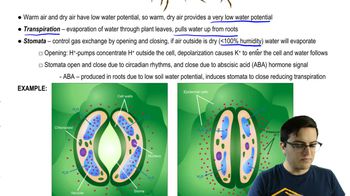
What important role does the Casparian strip play in the movement of water through plants?
a. Forces water to move through the cytoplasm of living endodermal cells as it makes its way from the soil to the xylem
b. Causes cells to shrink, thereby increasing pressure within cells
c. Loads sugars into xylem, thereby causing water to enter the xylem by osmosis
d. Acts as a filter that prevents salts, heavy metals, and other pollutants from entering root hairs