Compare and contrast the items in each pair:
(a) enhancers and the E. coli CAP binding site

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
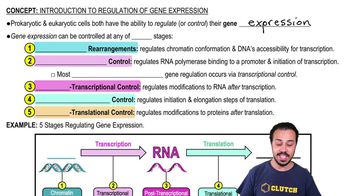

Compare and contrast the items in each pair:
(a) enhancers and the E. coli CAP binding site
Compare and contrast the items in each pair:
(b) promoter-proximal elements and the operator of the lac operon
Compare and contrast the items in each pair:
(c) general transcription factors and sigma.
The following statements are about the control of chromatin condensation. Select True or False for each.
T/F Reducing histone acetylase activity is likely to decrease gene transcription.
T/F Mutations that reduce the number of positively charged amino acids on histones should promote open chromatin.
T/F Chromatin remodeling complexes add chemical groups to histones.
T/F Adding an inhibitor of DNA methylation is likely to reduce gene transcription.
Predict how a mutation that caused continuous production of active p53 would affect the cell.
In the follow-up work to the experiment shown in Figure 19.6, the researchers used a technique that allowed them to see if two DNA sequences are in close physical proximity (association). They applied this method to examine how often an enhancer and the core promoter of the Hnf4a regulatory gene were near each other. A logical prediction is that compared with rats born to mothers fed a healthy diet, the Hnf4a gene in rats born to mothers fed a protein-poor diet would
a. Show no difference in how often the promoter and enhancer associated
b. Never show any promoter–enhancer association
c. Show a lower frequency of promoter–enhancer association
d. Show a higher frequency of promoter–enhancer association