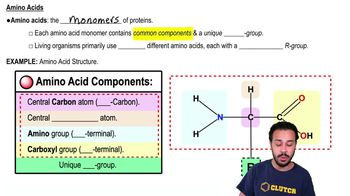
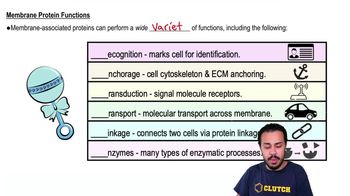
One of the possibilities considered about the genetic code was that the code was overlapping, meaning that a single base could be part of up to three codons. How many amino acids would be encoded in the sequence 5′-AUGUUACGGAAU-3′ by a non-overlapping and a maximally overlapping triplet code?
a. 4 (non-overlapping) and 16 (overlapping)
b. 4 and 12
c. 4 and 10
d. 12 and 4