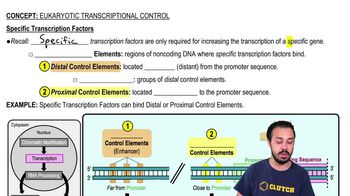
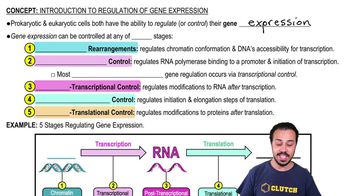
If a particular operon encodes enzymes for making an essential amino acid and is regulated like the trp operon, then
a. The amino acid inactivates the repressor.
b. The repressor is active in the absence of the amino acid.
c. The amino acid acts as a corepressor.
d. The amino acid turns on transcription of the operon.