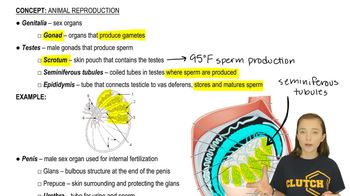
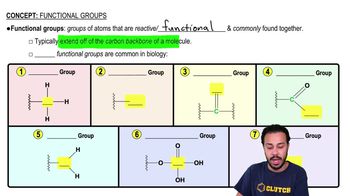
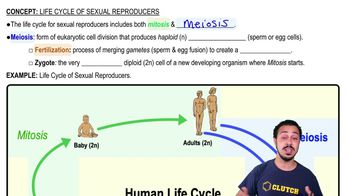
Which of the following characterizes parthenogenesis?
a. An individual may change its sex during its lifetime.
b. Specialized groups of cells grow into new individuals.
c. An organism is first a male and then a female.
d. An egg develops without being fertilized.