Peaks of LH and FSH production occur during
a. The menstrual flow phase of the uterine cycle
b. The beginning of the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle
c. The period just before ovulation
d. The secretory phase of the uterine cycle

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
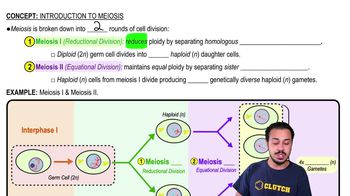
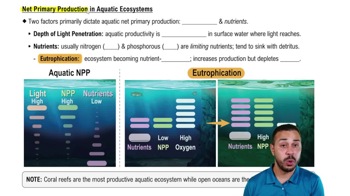
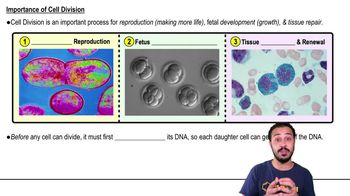
Peaks of LH and FSH production occur during
a. The menstrual flow phase of the uterine cycle
b. The beginning of the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle
c. The period just before ovulation
d. The secretory phase of the uterine cycle
During human gestation, rudiments of all organs develop
a. In the first trimester
b. In the second trimester
c. In the third trimester
d. During the blastocyst stage
Which of the following is a true statement?
a. All mammals have menstrual cycles
b. The endometrial lining is shed in menstrual cycles but reabsorbed in estrous cycles
c. Estrous cycles are more frequent than menstrual cycles
d. Ovulation occurs before the endometrium thickens in estrous cycles
Which statement about human reproduction is true?
a. Fertilization occurs in the vagina.
b. Spermatogenesis and oogenesis both require normal body temperature.
c. An oocyte completes meiosis after a sperm penetrates it.
d. The earliest stages of spermatogenesis occur closest to the lumen of the seminiferous tubules.