All fungi are
a. Symbiotic
b. Heterotrophic
c. Flagellated
d. Decomposers

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
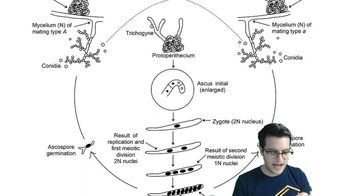

All fungi are
a. Symbiotic
b. Heterotrophic
c. Flagellated
d. Decomposers
The closest relatives of fungi are thought to be the
a. Animals
b. Vascular plants
c. Mosses
d. Slime molds
The most important adaptive advantage associated with the filamentous nature of fungal mycelia is
a. The ability to form haustoria and parasitize other organisms.
b. The potential to inhabit almost all terrestrial habitats.
c. The increased chance of contact between mating types.
d. An extensive surface area well suited for invasive growth and absorptive nutrition.
The grass Dichanthelium lanuginosum lives in hot soils and houses fungi of the genus Curvularia as endophytes. Researchers tested the impact of Curvularia on the heat tolerance of this grass. They grew plants without (E−) and with (E+) Curvularia endophytes at different temperatures and measured plant mass and the number of new shoots the plants produced. Draw a bar graph for plant mass versus temperature and interpret it.
Data from R. S. Redman et al., Thermotolerance generated by plant/fungal symbiosis, Science 298:1581 (2002).