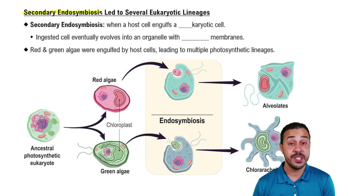
Plastids that are surrounded by more than two membranes are evidence of
a. Evolution from mitochondria.
b. Fusion of plastids.
c. Origin of the plastids from archaea.
d. Secondary endosymbiosis.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Plastids that are surrounded by more than two membranes are evidence of
a. Evolution from mitochondria.
b. Fusion of plastids.
c. Origin of the plastids from archaea.
d. Secondary endosymbiosis.
Biologists think that endosymbiosis gave rise to mitochondria before plastids partly because
a. The products of photosynthesis could not be metabolized without mitochondrial enzymes.
b. All eukaryotes have mitochondria (or their remnants), whereas many eukaryotes do not have plastids.
c. Mitochondrial DNA is less similar to prokaryotic DNA than is plastid DNA.
d. Without mitochondrial CO2 production, photosynthesis could not occur.
According to the phylogeny, which protists are in the same eukaryotic supergroup as plants?
a. Green algae
b. Dinoflagellates
c. Red algae
d. Both A and C
In a life cycle with alternation of generations, multicellular haploid forms alternate with
a. Unicellular haploid forms
b. Unicellular diploid forms
c. Multicellular haploid forms
d. Multicellular diploid forms
Based on the phylogenetic tree in Figure 28.5, which of the following statements is correct?
a. Excavata and SAR form a sister group
b. The most recent common ancestor of SAR is older than that of Unikonta
c. The most basal (first to diverge) eukaryotic supergroup cannot be determined
d. Excavata is the most basal eukaryotic supergroup