Textbook Question
Complete the following table:

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
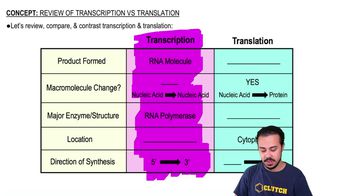
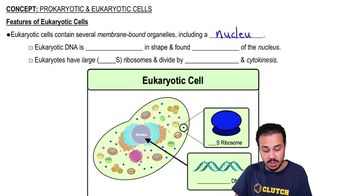
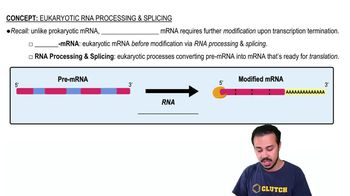
Complete the following table:
Which component is directly involved in translation?
A. RNA polymerase
B. ribosome
C. spliceosome
D. DNA
Using Figure 17.6, identify a 5′→3′ sequence of nucleotides in the DNA template strand for an mRNA coding for the polypeptide sequence Phe-Pro-Lys.
a. 5′-UUUCCCAAA-3′
b. 5′-GAACCCCTT-3′
c. 5′-CTTCGGGAA-3′
d. 5′-AAACCCUUU-3′
Which of the following mutations would be most likely to have a harmful effect on an organism?
a. A deletion of three nucleotides near the middle of a gene
b. A single nucleotide deletion in the middle of an intron
c. A single nucleotide deletion near the end of the coding sequence
d. A single nucleotide insertion downstream of, and close to, the start of the coding sequence