In the cells of some organisms, mitosis occurs without cytokinesis. This will result in
a. Cells with more than one nucleus
b. Cells that are unusually small
c. Cells lacking nuclei
d. Cell cycles lacking an S phase

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
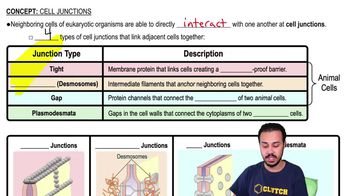
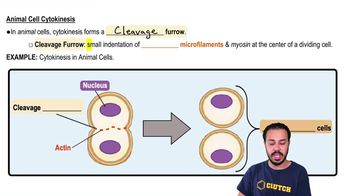

In the cells of some organisms, mitosis occurs without cytokinesis. This will result in
a. Cells with more than one nucleus
b. Cells that are unusually small
c. Cells lacking nuclei
d. Cell cycles lacking an S phase
Which of the following occurs during S phase?
a. Condensation of the chromosomes
b. Replication of the DNA
c. Separation of sister chromatids
d. Spindle formation
Cell A has half as much DNA as cells B, C, and D in a mitotically active tissue. Cell A is most likely in
a. G1
b. G2
c. Prophase
d. Metaphase
The light micrograph shows dividing cells near the tip of an onion root. Identify a cell in each of the following stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Describe the major events occurring at each stage.
<IMAGE>
Draw one eukaryotic chromosome as it would appear during interphase, during each of the stages of mitosis, and during cytokinesis. Also, draw and label the nuclear envelope and any microtubules attached to the chromosome(s).