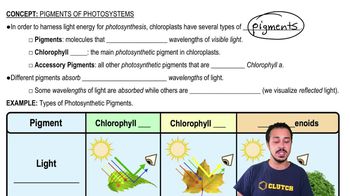
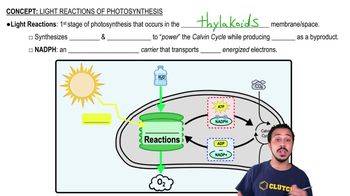
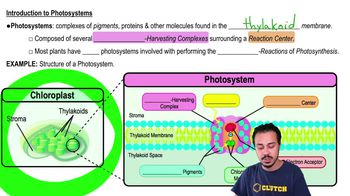
Textbook Question
Which of the following statements is a correct distinction between autotrophs and heterotrophs?
a. Autotrophs, but not heterotrophs, can nourish themselves beginning with CO2 and other nutrients that are inorganic.
b. Only heterotrophs require chemical compounds from the environment.
c. Cellular respiration is unique to heterotrophs.
d. Only heterotrophs have mitochondria.