The light reactions of photosynthesis supply the Calvin cycle with
a. Light energy.
b. CO2 and ATP.
c. H2O and NADPH.
d. ATP and NADPH.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
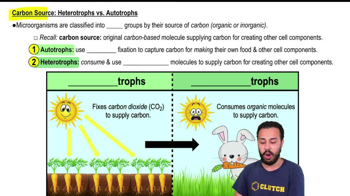

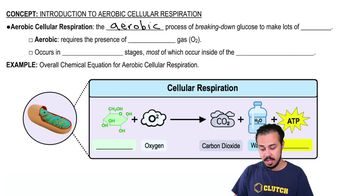
The light reactions of photosynthesis supply the Calvin cycle with
a. Light energy.
b. CO2 and ATP.
c. H2O and NADPH.
d. ATP and NADPH.
Which of the following sequences correctly represents the flow of electrons during photosynthesis?
a. NADPH → O2 → CO2
b. H2O → NADPH → Calvin cycle
c. H2O → photosystem I → photosystem II
d. NADPH → electron transport chain → O2
How is photosynthesis similar in C4 plants and CAM plants?
a. In both cases, only photosystem I is used.
b. Both types of plants make sugar without the Calvin cycle.
c. In both cases, rubisco is not used to fix carbon initially.
d. Both types of plants make most of their sugar in the dark.
Which of the following occurs during the Calvin cycle?
a. Carbon fixation
b. Reduction of NADP+
c. Release of oxygen
d. Generation of CO₂
In mechanism, photophosphorylation is most similar to
a. Substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis.
b. Oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration.
c. Carbon fixation.
d. Reduction of NADP+.
Which process is most directly driven by light energy?
a. Creation of a pH gradient by pumping protons across the thylakoid membrane
b. Reduction of NADP+ molecules
c. Transfer of energy from pigment molecule to pigment molecule
d. ATP synthesis