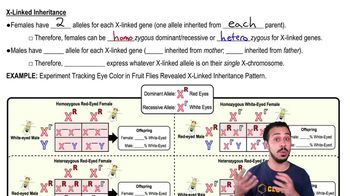
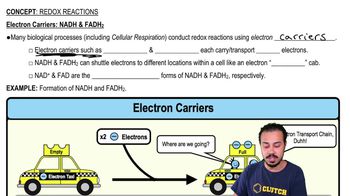
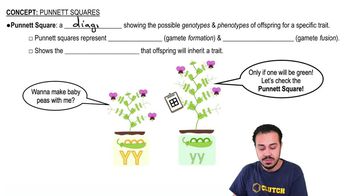
Scientists have recently developed a process by which a skin cell from a human can be triggered to develop into a human heart muscle cell. This is possible because ________.
a. Most cells in the human body contain the genetic instructions for making all types of human cells.
b. A skin cell is produced when all genes in the cell are expressed; turning off some genes in the cell results in a heart cell.
c. Scientists can add new genes to old cells to make them take different forms.
d. A skin cell expresses only recessive alleles, so it can be triggered to produce dominant heart cell alleles.
e. It is easy to mutate the genes in skin cells to produce the alleles required for other cell types.