Add labels to the figure that follows, which illustrates female internal reproductive organs.

An egg cell that is not fertilized follows which path?
a. Ovary, oviduct, uterus, cervix
b. Ovary, uterus, oviduct, cervix
c. Oviduct, ovary, cervix, uterus
d. Oviduct, ovary, uterus, cervix
e. Ovary, oviduct, cervix, uterus
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
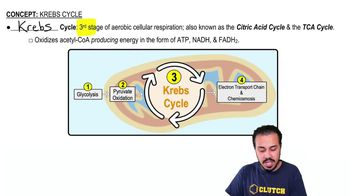
Key Concepts
Ovarian Cycle
Reproductive Tract Pathway
Menstrual Cycle and Shedding

What happens to the egg cell and the remains of the tissue it developed in at ovulation?
A sperm cell follows which path?
a. Seminiferous tubules, epididymis, vas deferens, urethra
b. Urethra, vas deferens, seminiferous tubules, epididymis
c. Seminiferous tubules, vas deferens, epididymis, urethra
d. Epididymis, seminiferous tubules, vas deferens, urethra
e. Epididymis, vas deferens, seminiferous tubules, urethra
Which of the following is mismatched?
a. Urethra: sperm passage
b. Testes: hormone production
c. Vas deferens: semen production
d. Seminiferous tubules: sperm production
The production of gametes ________.
a. Begins at puberty in males and females.
b. Requires that the testes of males produce semen.
c. Results in the production of diploid cells from haploid cells.
d. Begins at puberty in females.
e. Produces sperm and eggs that carry half the number of chromosomes as nongametes.
If humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, each carrying hundreds to thousands of genes, roughly how many genes are there in the human genome?
a. 23
b. 46
c. 1000
d. 20,000
e. 200,000
