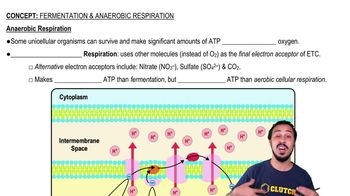
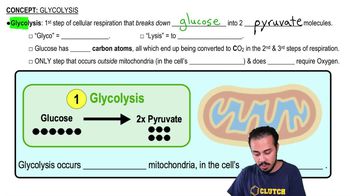
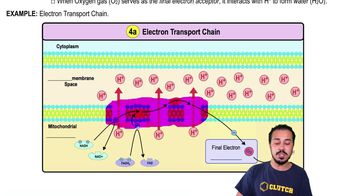
Cellular respiration involves ________.
a. The aerobic metabolism of sugars in the mitochondria by a process called glycolysis.
b. An electron transport chain that releases carbon dioxide.
c. The synthesis of ATP, which is driven by the rushing of protons through an ATP synthase.
d. Electron carriers that bring electrons to the citric acid cycle; e. the production of water during the citric acid cycle.