Micronutrients ________.
a. Include vitamins and carbohydrates.
b. Are not metabolized to produce energy.
c. Contain more energy than fatty acids.
d. Can be synthesized by most cells.

 Belk, Maier 6th Edition
Belk, Maier 6th Edition Ch. 3 - Is It Possible to Supplement Your Way to Better Performance and Health?
Ch. 3 - Is It Possible to Supplement Your Way to Better Performance and Health? Problem 8
Problem 8 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Micronutrients ________.
a. Include vitamins and carbohydrates.
b. Are not metabolized to produce energy.
c. Contain more energy than fatty acids.
d. Can be synthesized by most cells.
The main constituents of the plasma membrane are ________.
a. Carbohydrates and lipids
b. Proteins and phospholipids
c. Fats and carbohydrates
d. Fatty acids and nucleic acids
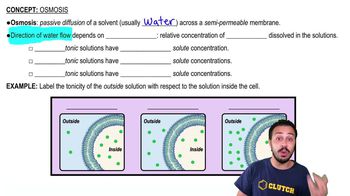
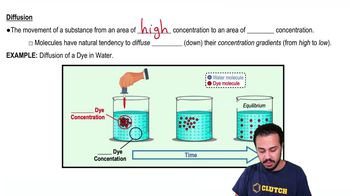
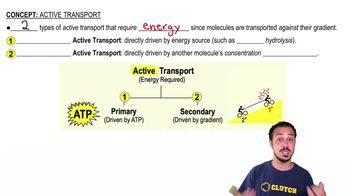
A substance moving across a membrane against a concentration gradient is moving by ________.
a. Passive transport
b. Osmosis
c. Facilitated diffusion
d. Active transport
e. Diffusion
Which of the following forms of membrane transport require specific membrane proteins?
a. Diffusion
b. Exocytosis
c. Facilitated diffusion
d. Active transport
e. Facilitated diffusion and active transport
Which of the following cannot pass through the membrane without the help of a membrane protein?
a. Carbon dioxide
b. Water
c. Oxygen
d. Charged molecules