Transcription ________.
a. Synthesizes new daughter DNA molecules from an existing DNA molecule
b. Results in the synthesis of an RNA copy of a gene
c. Pairs thymines (T) with adenines (A)
d. Occurs on ribosomes

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Transcription ________.
a. Synthesizes new daughter DNA molecules from an existing DNA molecule
b. Results in the synthesis of an RNA copy of a gene
c. Pairs thymines (T) with adenines (A)
d. Occurs on ribosomes
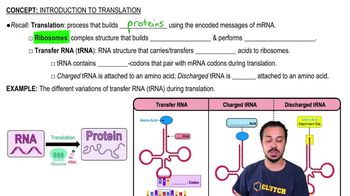
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
a. Carries monosaccharides to the ribosome for synthesis
b. Is made of messenger RNA
c. Has an anticodon region that is complementary to the mRNA codon
d. Is the site of protein synthesis
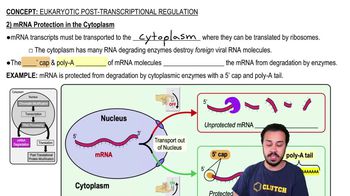
During the process of transcription, ________.
a. DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of more DNA.
b. DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of RNA.
c. DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of proteins.
d. RNA serves as a template for the synthesis of proteins.
The RNA polymerase enzyme binds to ________, initiating transcription.
a. Amino acids
b. tRNA
c. The promoter sequence
d. The ribosome
A particular triplet of bases in the coding sequence of DNA is TGA. The anticodon on the tRNA that binds to the mRNA codon is ________.
a. TGA
b. UGA
c. UCU
d. ACU
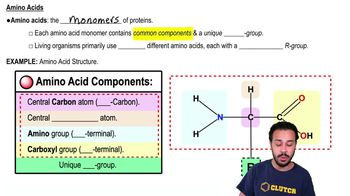
RNA and DNA are similar because ________.
a. Both are double-stranded helices.
b. Uracil is found in both of them.
c. Both contain the sugar deoxyribose.
d. Both are made up of nucleotides consisting of a sugar, a phosphate, and a base.