Textbook Question
Translation results in the production of ________.
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. Protein
d. Individual amino acids
e. Transfer RNA molecules

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
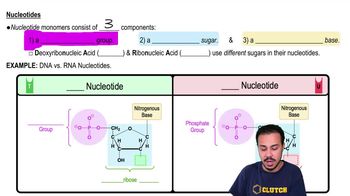
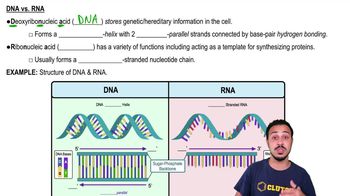
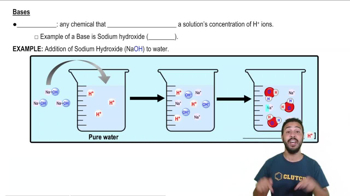
Translation results in the production of ________.
a. RNA
b. DNA
c. Protein
d. Individual amino acids
e. Transfer RNA molecules
The RNA polymerase enzyme binds to ________, initiating transcription.
a. Amino acids
b. tRNA
c. The promoter sequence
d. The ribosome
A particular triplet of bases in the coding sequence of DNA is TGA. The anticodon on the tRNA that binds to the mRNA codon is ________.
a. TGA
b. UGA
c. UCU
d. ACU
Add labels to the figure that follows, which illustrates a transfer RNA molecule.