Back
Back Frederic H. Martini, Judi L. Nath, Edwin F. Bartholomew 11th Edition
Frederic H. Martini, Judi L. Nath, Edwin F. Bartholomew 11th Edition Ch. 2 The Chemical Level of Organization
Ch. 2 The Chemical Level of OrganizationProblem 1a
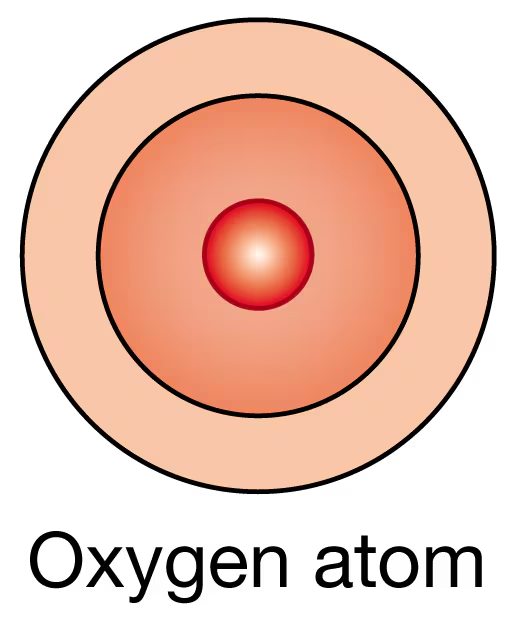
An oxygen atom has eight protons.
(a) Sketch in the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus of the oxygen atom in the following diagram.
Problem 1b
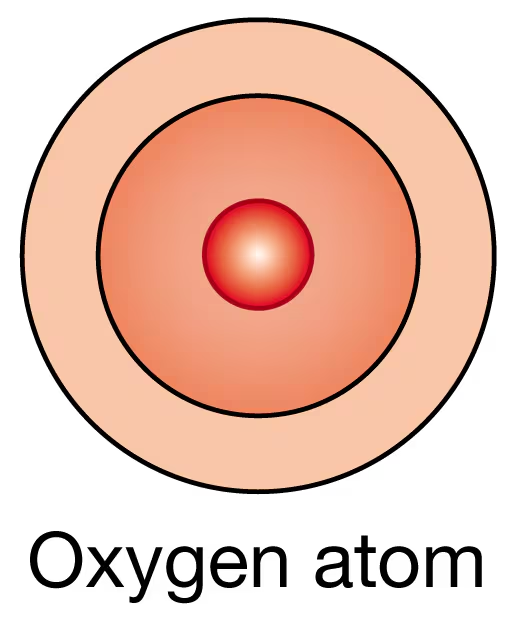
An oxygen atom has eight protons.
(b) How many more electrons will it take to fill the outermost energy level?
Problem 2
What is the following type of decomposition reaction called?
ABCD + H₂O → ABCH + DOH
Problem 3
The subatomic particle with the least mass
(a) Carries a negative charge
(b) Carries a positive charge
(c) Plays no part in the atom's chemical reactions
(d) Is found only in the nucleus
Problem 4
Isotopes of an element differ from each other in the number of
(a) Protons in the nucleus
(b) Neutrons in the nucleus
(c) Electrons in the outer shells
(d) a, b, and c are all correct
Problem 5
The number and arrangement of electrons in an atom's outer energy level (valence shell) determine the atom's
(a) Atomic weight
(b) Atomic number
(c) Molecular weight
(d) Chemical properties
Problem 6
All organic compounds in the human body contain all of the following elements except
(a) Hydrogen
(b) Oxygen
(c) Carbon
(d) Calcium
(e) Both a and d
Problem 7
A substance containing atoms of different elements that are bonded together is called a(n)
(a) Molecule
(b) Compound
(c) Mixture
(d) Isotope
(e) Solution
Problem 8
All the chemical reactions that occur in the human body are collectively referred to as
(a) Anabolism
(b) Catabolism
(c) Metabolism
(d) Homeostasis
Problem 9
Which of the following chemical equations illustrates a typical decomposition reaction?
a. A + B → AB
b. AB + CD → AD + CB
c. 2A₂+ B₂ → 2A₂B
d. AB → A + B
Problem 10
The speed, or rate, of a chemical reaction is influenced by
(a) The presence of catalysts
(b) The temperature
(c) The concentration of the reactants
(d) a, b, and c are all correct
Problem 11
A pH of 7.8 in the human body typifies a condition referred to as
(a) Acidosis
(b) Alkalosis
(c) Dehydration
(d) Homeostasis
Problem 12
A(n)__is a solute that dissociates to release hydrogen ions, and a(n)___is a solute that removes hydrogen ions from solution.
(a) base, acid
(b) salt, base
(c) acid, salt
(d) acid, base
Problem 13
Special catalytic molecules called___speed up chemical reactions in the human body.
(a) enzymes
(b) cytozymes
(c) cofactors
(d) activators
(e) cytochromes
Problem 14
Which of the following is not a function of a protein?
(a) Support
(b) Transport
(c) Metabolic regulation
(d) Storage of genetic information
(e) Movement
Problem 15
Complementary base pairing in DNA includes the pairs
(a) Adenine–uracil and cytosine–guanine
(b) Adenine–thymine and cytosine–guanine
(c) Adenine–guanine and cytosine–thymine
(d) Guanine–uracil and cytosine–thymine
Problem 16
What are the three subatomic particles in atoms?
Problem 17
What four major classes of organic compounds (polymers) are found in the body?
Problem 18
List three important functions of triglycerides (neutral fats) in the body.
Problem 19
List seven major functions performed by proteins.
Problem 20a
a. What three basic components make up a nucleotide of DNA?
Problem 20b
b. What three basic components make up a nucleotide of RNA?
Problem 21
What three components are required to create the high-energy compound ATP?
Problem 22
If a polypeptide contains 10 peptide bonds, how many amino acids does it contain?
(a) 9
(b) 10
(c) 11
(d) 12
Problem 23
A dehydration synthesis reaction between glycerol and a single fatty acid would yield a(n)
(a) Micelle
(b) Omega-3 fatty acid
(c) Triglyceride
(d) Monoglyceride
(e) Diglyceride
Problem 24
Explain how enzymes function in chemical reactions.
Problem 25
What is a salt? How does a salt differ from an acid or a base?
Problem 26
Explain the differences among nonpolar covalent bonds, polar covalent bonds, and ionic bonds.
Problem 27
In an exergonic reaction,
(a) Large molecules are broken down into smaller ones.
(b) Small molecules are assembled into larger ones.
(c) Molecules are rearranged to form new molecules.
(d) Molecules move from reactants to products and back.
(e) Energy is released during the reaction.
Problem 28
The hydrogen bonding that occurs in water is responsible for all of the following except
(a) The high boiling point of water
(b) The low freezing point of water
(c) The ability of water to dissolve nonpolar substances
(d) The ability of water to dissolve inorganic salts
(e) The surface tension of water