Back
BackProblem 1
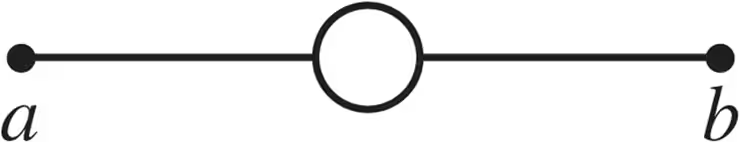
A uniform wire of resistance R is cut into three equal lengths. One of these is formed into a circle and connected between the other two (Fig. E26.1). What is the resistance between the opposite ends a and b?
Problem 2
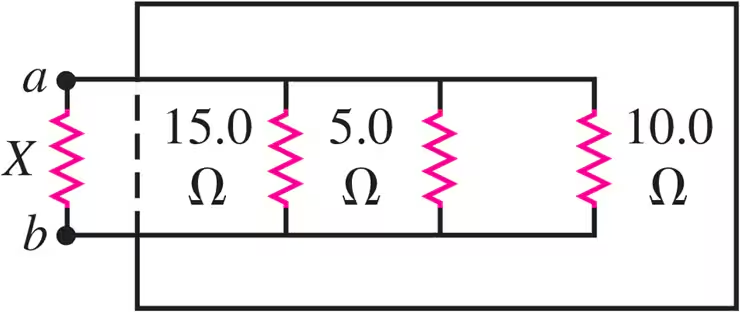
A machine part has a resistor X protruding from an opening in the side. This resistor is connected to three other resistors, as shown in Fig. E26.2. An ohmmeter connected across a and b reads 2.00 Ω. What is the resistance of X?
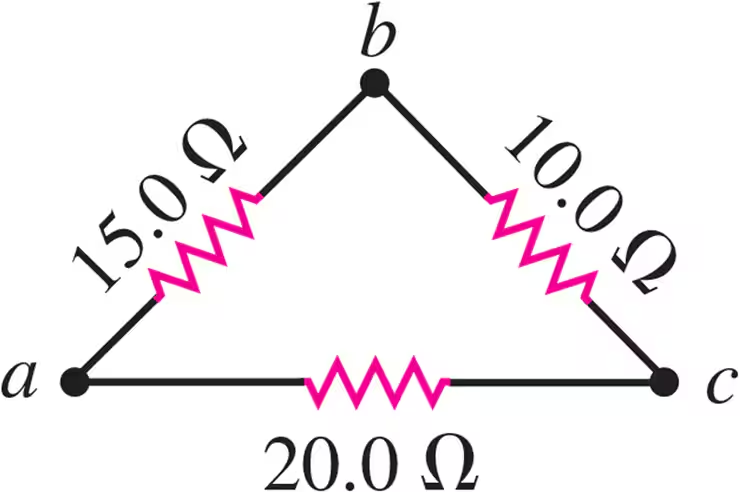
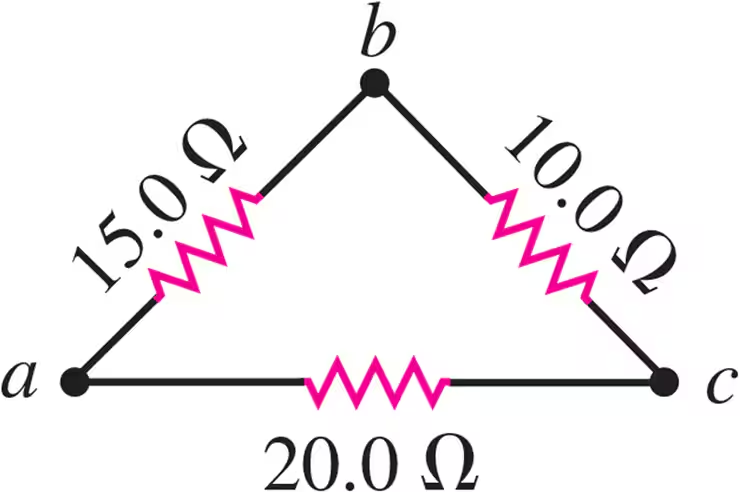
Problem 5a
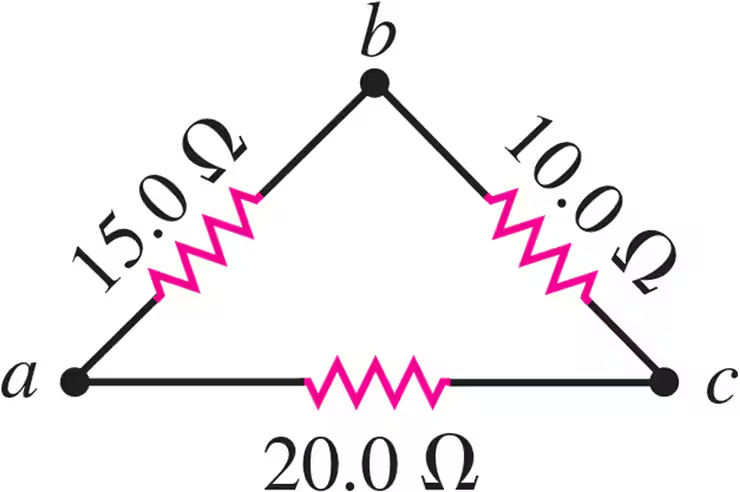
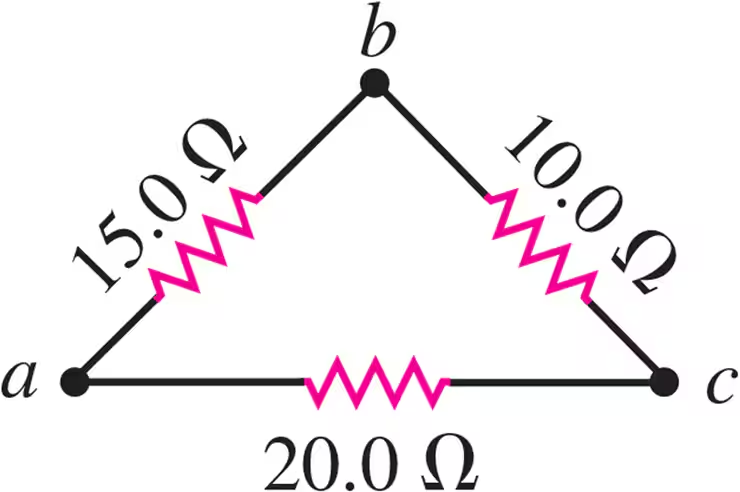
A triangular array of resistors is shown in Fig. E26.5. What current will this array draw from a 35.0 V battery having negligible internal resistance if we connect it across ab?
Problem 5b
A triangular array of resistors is shown in Fig. E26.5. What current will this array draw from a 35.0 V battery having negligible internal resistance if we connect it across bc?
Problem 5c
A triangular array of resistors is shown in Fig. E26.5. What current will this array draw from a 35.0 V battery having negligible internal resistance if we connect it across ac?
Problem 5d
A triangular array of resistors is shown in Fig. E26.5. If the battery has an internal resistance of 3.00Ω, what current will the array draw if the battery is connected across bc?
Problem 10a
Power Rating of a Resistor. The power rating of a resistor is the maximum power the resistor can safely dissipate without too great a rise in temperature and hence damage to the resistor. If the power rating of a 15 kΩ resistor is 5.0 W, what is the maximum allowable potential difference across the terminals of the resistor?
Problem 10b
Power Rating of a Resistor. The power rating of a resistor is the maximum power the resistor can safely dissipate without too great a rise in temperature and hence damage to the resistor. A 9.0 kΩ resistor is to be connected across a 120 V potential difference. What power rating is required?
Problem 10c
Power Rating of a Resistor. The power rating of a resistor is the maximum power the resistor can safely dissipate without too great a rise in temperature and hence damage to the resistor. A 100.0 Ω and a 150.0 Ω resistor, both rated at 2.00 W, are connected in series across a variable potential difference. What is the greatest this potential difference can be without overheating either resistor, and what is the rate of heat generated in each resistor under these conditions?
Problem 21a
Light Bulbs in Series and in Parallel. Two light bulbs have constant resistances of 400Ω and 800Ω. If the two light bulbs are connected in series across a 120-V line, find the current through each bulb.
Problem 21b
Light Bulbs in Series and in Parallel. Two light bulbs have constant resistances of 400Ω and 800Ω. If the two light bulbs are connected in series across a 120 V line, find the power dissipated in each bulb.
Problem 21c
Light Bulbs in Series and in Parallel. Two light bulbs have constant resistances of 400Ω and 800Ω. If the two light bulbs are connected in series across a 120 V line, find the total power dissipated in both bulbs.
Problem 21d
Light Bulbs in Series and in Parallel. Two light bulbs have constant resistances of 400Ω and 800Ω. The two light bulbs are now connected in parallel across the 120 V line. Find the current through each bulb.
Problem 21e
Light Bulbs in Series and in Parallel. Two light bulbs have constant resistances of 400Ω and 800Ω. The two light bulbs are now connected in parallel across the 120 V line. Find the power dissipated in each bulb.
Problem 21f
Light Bulbs in Series and in Parallel. Two light bulbs have constant resistances of 400Ω and 800Ω. The two light bulbs are now connected in parallel across the 120 V line. Find the total power dissipated in both bulbs.
Problem 21g
Light Bulbs in Series and in Parallel. Two light bulbs have constant resistances of 400Ω and 800Ω. The two light bulbs are connected in series across a 120 V line. Afterwards, the two light bulbs are connected in parallel across the 120 V line. In each situation, which of the two bulbs glows the brightest?
Problem 21h
Light Bulbs in Series and in Parallel. Two light bulbs have constant resistances of 400Ω and 800Ω. The two light bulbs are connected in series across a 120 V line. Afterwards, the two light bulbs are connected in parallel across the 120 V line. In which situation is there a greater total light output from both bulbs combined?
Problem 23a
In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.23, ammeter A1 reads 10.0 A and the batteries have no appreciable internal resistance. What is the resistance of R?
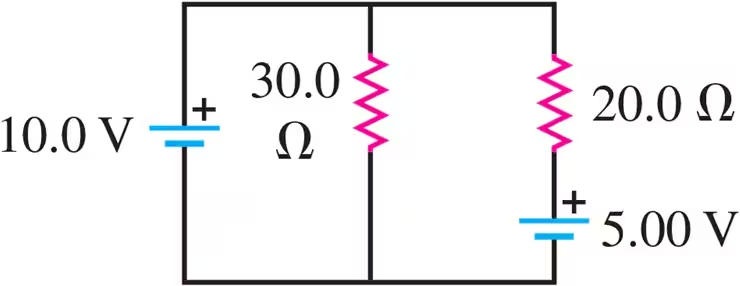
Problem 24a
The batteries shown in the circuit in Fig. E26.24 have negligibly small internal resistances. Find the current through the 30.0-Ω resistor.
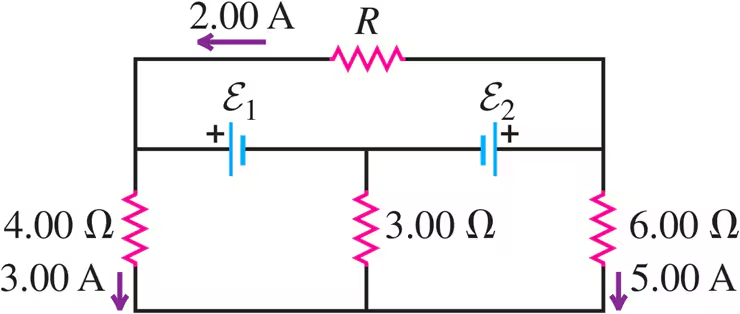
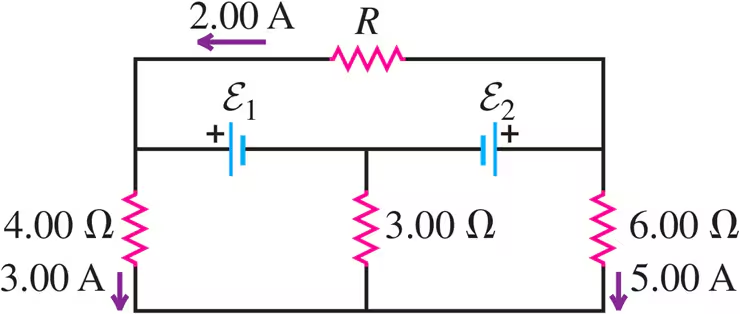
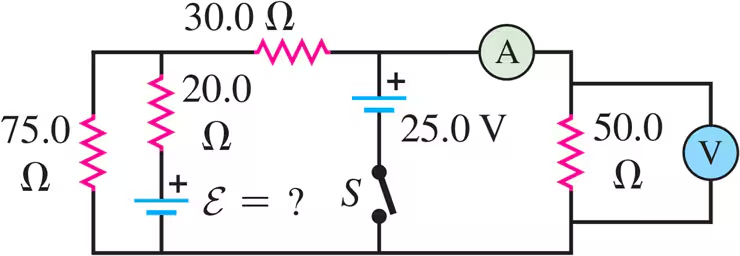
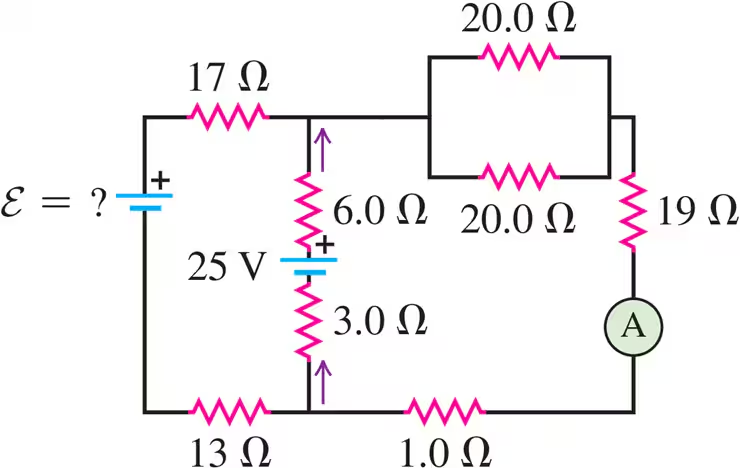
Problem 26
Find the emfs and in the circuit of Fig. E26.26, and find the potential difference of point relative to point .
Problem 27a
In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.27 find the current in the 3.00 Ω resistor.
Problem 27b
In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.27 find the unknown emfs and .
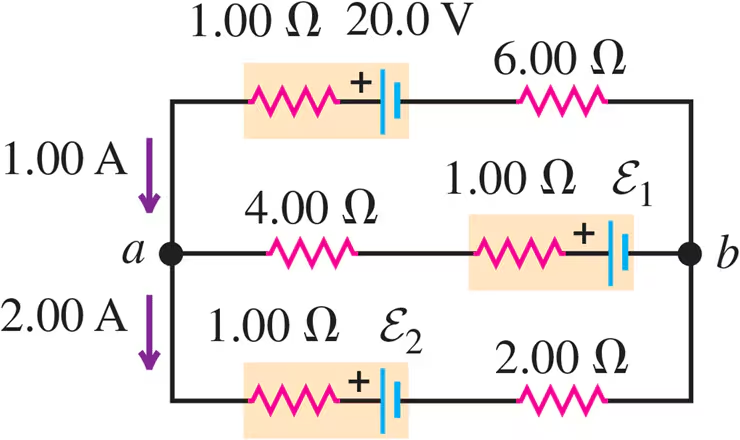
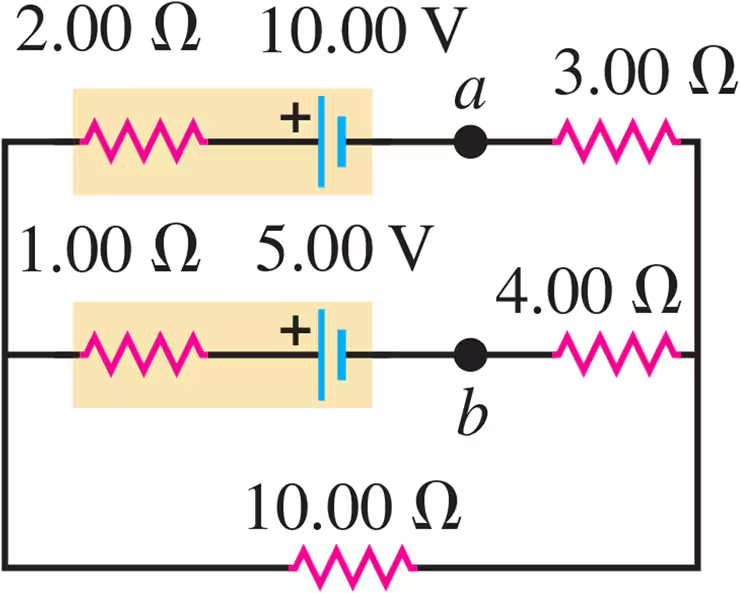
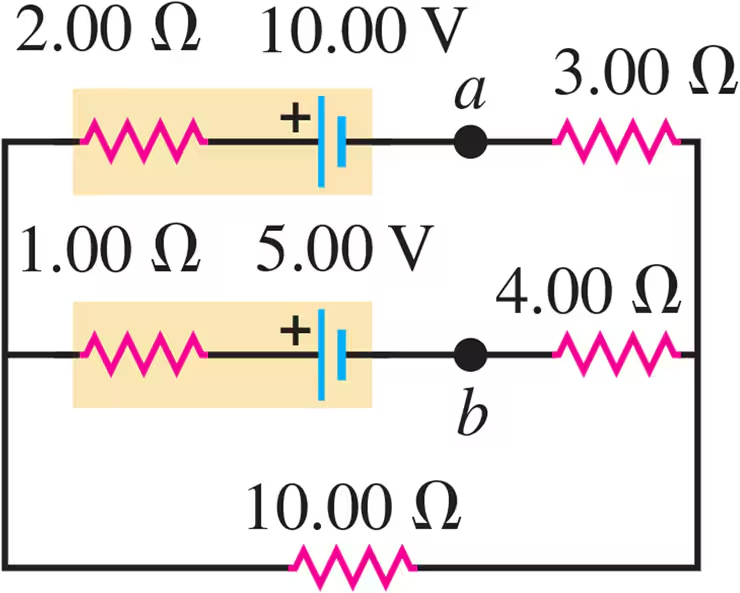
Problem 29a
The 10.00 V battery in Fig. E26.28 is removed from the circuit and reinserted with the opposite polarity, so that its positive terminal is now next to point a. The rest of the circuit is as shown in the figure. Find the current in each branch.
Problem 30a
The 5.00 V battery in Fig. E26.28 is removed from the circuit and replaced by a 15.00 V battery, with its negative terminal next to point b. The rest of the circuit is as shown in the figure. Find the current in each branch.
Problem 31b
In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.31 the batteries have negligible internal resistance and the meters are both idealized. With the switch S open, the voltmeter reads 15.0 V. What will the ammeter read when the switch is closed?
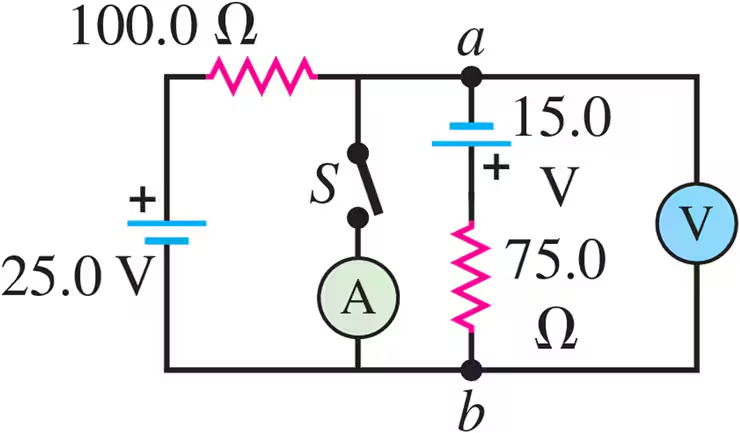
Problem 33a
In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.33 all meters are idealized and the batteries have no appreciable internal resistance. Find the reading of the voltmeter with the switch S open. Which point is at a higher potential: a or b?
Problem 34b
In the circuit shown in Fig. E26.34, the 6.0 Ω resistor is consuming energy at a rate of 24 J/s when the current through it flows as shown. What are the polarity and emf ε of the unknown battery, assuming it has negligible internal resistance?
Problem 45
An emf source with ε = 120V, a resistor with R = 80.0Ω, and a capacitor with C = 4.00 μF are connected in series. As the capacitor charges, when the current in the resistor is 0.900 A, what is the magnitude of the charge on each plate of the capacitor?
Problem 52b
The heating element of an electric dryer is rated at 4.1 kW when connected to a 240 V line. What is the resistance of the dryer's heating element at its operating temperature?
Problem 53
A 1500 W electric heater is plugged into the outlet of a 120 V circuit that has a 20 A circuit breaker. You plug an electric hair dryer into the same outlet. The hair dryer has power settings of 600 W, 900 W, 1200 W, and 1500 W. You start with the hair dryer on the 600 W setting and increase the power setting until the circuit breaker trips. What power setting caused the breaker to trip?