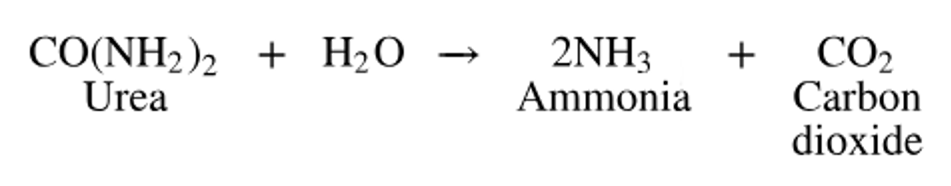Back
BackProblem 1
Radioisotopes are frequently used to label molecules in a cell. The fate of atoms and molecules in a cell can then be followed. This process is the basis for the following question.
Assume E. coli bacteria are grown in a nutrient medium containing the radioisotope 16N. After a 48-hour incubation period, the 16N would most likely be found in the E. coli’s
a. Carbohydrates.
b. Lipids.
c. Proteins.
d. Water.
e. None of the above
Problem 1
What is a chemical element?
Problem 2
Radioisotopes are frequently used to label molecules in a cell. The fate of atoms and molecules in a cell can then be followed. This process is the basis for the following question.
If Pseudomonas bacteria are supplied with radioactively labeled cytosine, after a 24-hour incubation period this cytosine would most likely be found in the cells’
a. Carbohydrates.
b. DNA.
c. Lipids.
d. Water.
e. Proteins.
Problem 2
Diagram the electronic configuration of a carbon atom.
Problem 3
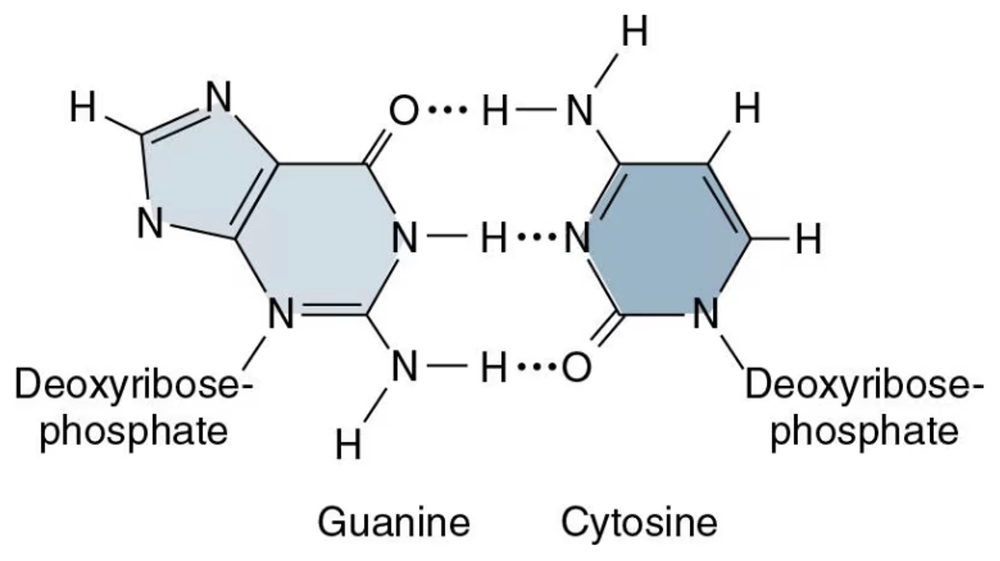
What type of bond holds the following atoms together?
a. Li+ and Cl- in LiCl
b. Carbon and oxygen atoms in methanol
c. Oxygen atoms in O2
d. A hydrogen atom of one nucleotide to a nitrogen or oxygen atom of another nucleotide in:
Problem 3
Radioisotopes are frequently used to label molecules in a cell. The fate of atoms and molecules in a cell can then be followed. This process is the basis for the following question.
If E. coli were grown in a medium containing the radioactive isotope 32P, the 32P would be found in all of the following molecules of the cell except
a. ATP.
b. Carbohydrates.
c. DNA.
d. Plasma membrane.
e. Complex lipids.
Problem 4
The optimum pH of Acidithiobacillus bacteria (pH 3) is _______________ times more acid than blood (pH 7).
a. 4
b. 10
c. 100
d. 1000
e. 10,000
Problem 4
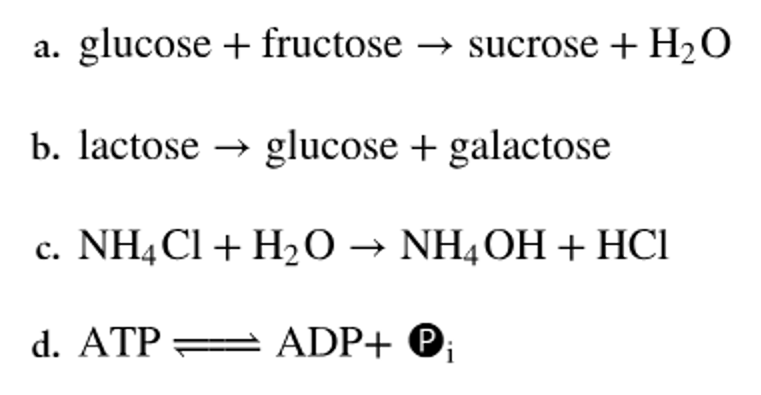
Classify the following types of chemical reactions.
Problem 5
Bacteria use the enzyme urease to obtain nitrogen in a form they can use from urea in the following reaction:
What purpose does the enzyme serve in this reaction? What type of reaction is this?
Problem 5
The best definition of ATP is that it is
a. A molecule stored for food use.
b. A molecule that supplies energy to do work.
c. A molecule stored for an energy reserve.
d. A molecule used as a source of phosphate.
Problem 6
Which of the following is an organic molecule?
a. H2O (water)
b. O2 (oxygen)
c. C18H29SO3
d. FeO (iron oxide)
e. F2C=CF2 (Teflon)
Problem 6
Classify the following as subunits of either a carbohydrate, lipid, protein, or nucleic acid.
a. <IMAGE>
b. <IMAGE>
c. <IMAGE>
d. Thymine nucleotide
Problem 7
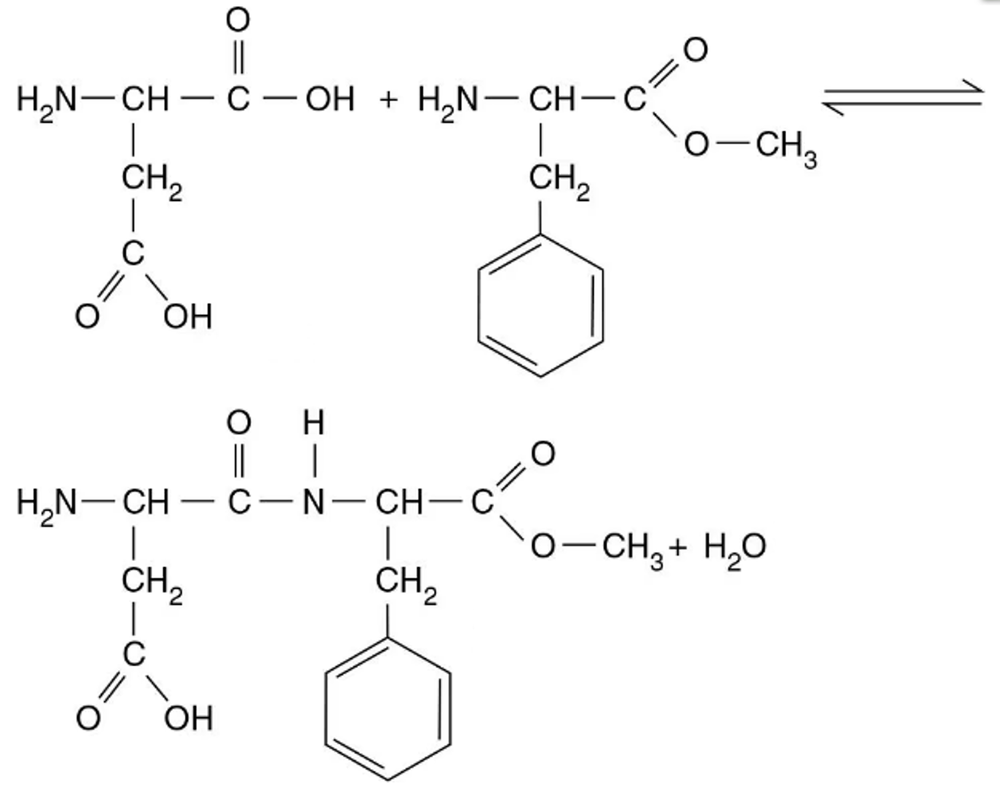
The artificial sweetener aspartame, or NutraSweet®, is made by joining aspartic acid to methylated phenylalanine, as shown in the following.
a. What types of molecules are aspartic acid and phenylalanine?
b. What direction is the hydrolysis reaction (left to right or right to left)?
c. What direction is the dehydration synthesis reaction?
d. Circle the atoms involved in the formation of water.
e. Identify the peptide bond.
Problem 7
Classify each of the molecules on the left as an acid, base, or salt. The dissociation products of the molecules are shown to help you.
HNO3 → H+ + NO⁻3
a. Acid
b. Base
c. Salt
Problem 8
Classify each of the molecules on the left as an acid, base, or salt. The dissociation products of the molecules are shown to help you.
H2SO4 → 2H+ + SO42⁻
a. Acid
b. Base
c. Salt
Problem 8
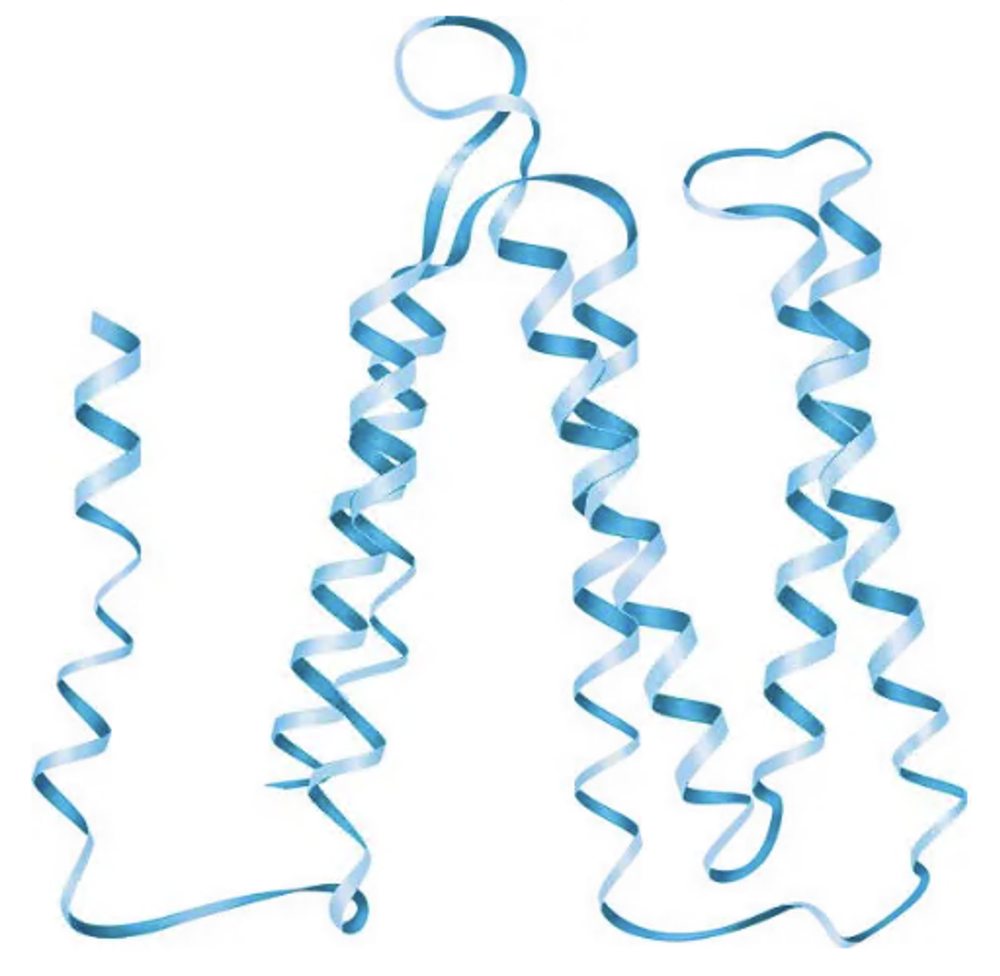
The following diagram shows the bacteriorhodopsin protein. Indicate the regions of primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. Does this protein have quaternary structure?
Problem 9
Draw a simple lipid, and show how it could be modified to a phospholipid.
Problem 9
Classify each of the molecules on the left as an acid, base, or salt. The dissociation products of the molecules are shown to help you.
NaOH → Na⁺ + OH⁻
a. Acid
b. Base
c. Salt
Problem 10
What type of microorganism has a chitin cell wall, has DNA that is contained in a nucleus, and has ergosterol in its plasma membrane?
Problem 10
Classify each of the molecules on the left as an acid, base, or salt. The dissociation products of the molecules are shown to help you.
MgSO4 → Mg2+ + SO42⁻
a. Acid
b. Base
c. Salt