Back
BackProblem 57c
Using energy values from TABLE 3.8, determine each of the following:
c. If Charles consumes 1800 kcal per day, he will maintain his weight. Would he lose weight on his new diet?
Problem 57d
Using energy values from TABLE 3.8, determine each of the following:
d. If expending 3500 kcal is equal to a loss of 1.0 lb, how many days will it take Charles to lose 5.0 lb?
Problem 58b
For the amount of exercise that Charles did for one week in part a, if expending 3500 kcal is equal to a loss of 1.0 lb, how many pounds did he lose?
Problem 66
After a week, biochemical reactions in compost slow, and the temperature drops to 45 °C. The dark brown organic-rich mixture is ready for use in the garden. What is this temperature in degrees Fahrenheit? In kelvins? (3.3)
Problem 67
Calculate the energy to heat two cubes (gold and aluminum) each with a volume of 10 cm3 from 15 °C to 25 °C. Refer to Tables 2.8 and 3.11.
Problem 69d
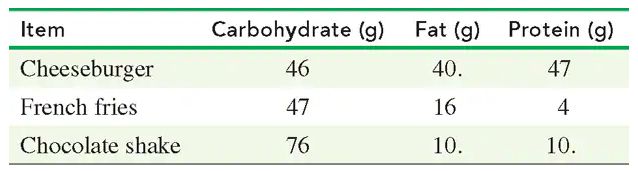
A 70.0-kg person had a quarter-pound cheeseburger, french fries, and a chocolate shake.
<IMAGE>
d. Using TABLE 3.10, determine the number of hours of running needed to burn off the kilocalories in this meal.
Problem 72b
Classify each of the following as an element, a compound, or a mixture:
b. a salad dressing of oil and vinegar
Problem 73b
Classify each of the following mixtures as homogeneous or heterogeneous:
b. herbal tea
Problem 73c
Classify each of the following mixtures as homogeneous or heterogeneous:
c. vegetable oil
Problem 77c
Identify each of the following as a physical or chemical property:
c. Gold is a good conductor of electricity.
Problem 80a
Identify each of the following as a physical or chemical change:
a. Aspirin tablets are broken in half.
Problem 82a
Calculate each of the following temperatures in kelvins and degrees Fahrenheit:
a. The highest recorded temperature in the world was 58.0 °C in El Azizia, Libya, on September 13, 1922.
Problem 82b
Calculate each of the following temperatures in kelvins and degrees Fahrenheit:
b. The lowest recorded temperature in the world was –89.2 °C in Vostok, Antarctica, on July 21, 1983.
Problem 83
What is –15 °F in degrees Celsius and in kelvins?
Problem 87
On a hot day, the beach sand gets hot but the water stays cool. Would you predict that the specific heat of sand is higher or lower than that of water? Explain.
<IMAGE>
Problem 89
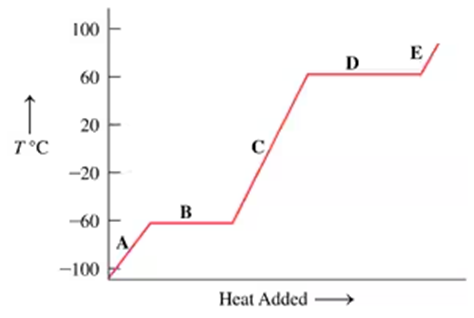
The following graph is a heating curve for chloroform, a solvent for fats, oils, and waxes:
d. At the following temperatures, is chloroform a solid, liquid, or gas?
–80 °C, –40 °C; 25 °C; 80 °C
Problem 95
A hot-water bottle for a patient contains 725 g of water at 65 °C. If the water cools to body temperature (37 °C), how many kilojoules of heat could be transferred to sore muscles?
Problem 97
When a 0.66-g sample of olive oil is burned in a calorimeter, the heat released increases the temperature of 370 g of water from 22.7 °C to 38.8 °C. What is the energy value for the olive oil in kcal/g?
Problem 98
A 45-g piece of ice at 0.0 °C is added to a sample of water at 8.0 °C. All of the ice melts and the temperature of the water decreases to 0.0 °C. How many grams of water were in the sample?
Problem 99a
In a large building, oil is used in a steam boiler heating system. The combustion of 1.0 lb of oil provides 2.4 × 107 J.
a. How many kilograms of oil are needed to heat 150 kg of water from 22 °C to 100 °C?
Problem 99b
In a large building, oil is used in a steam boiler heating system. The combustion of 1.0 lb of oil provides 2.4 × 107 J.
b. How many kilograms of oil are needed to change 150 kg of water to steam at 100 °C?
Problem 100b
When 1.0 g of gasoline burns, it releases 11 kcal. The density of gasoline is 0.74 g/mL.
b. If a television requires 150 kJ/h to run, how many hours can the television run on the energy provided by 1.0 gal of gasoline?
Problem 105b
A metal is thought to be titanium or aluminum. When 4.7 g of the metal absorbs 11 J, its temperature rises by 4.5 °C.
b. Would you identify the metal as titanium or aluminum (see TABLE 3.11)?
Problem 106a
A metal is thought to be copper or gold. When 18 g of the metal absorbs 58 cal, its temperature rises by 35 °C.
a. What is the specific heat, in cal/g °C, of the metal?