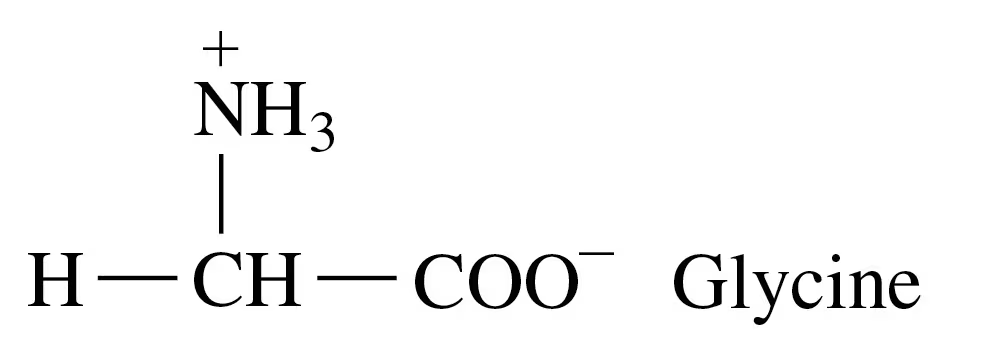Back
BackProblem 55a
What is the ATP energy yield associated with each of the following?
a. NADH → NAD+
Problem 55c
What is the ATP energy yield associated with each of the following?
c. 2 pyruvate → 2 acetyl CoA + 2CO2
Problem 56a
What is the ATP energy yield associated with each of the following?
a. FADH2 → FAD
Problem 57a
Caprylic acid, CH3 ― (CH2)6 ― COOH, is a C8 fatty acid found in milk.
a. State the number of β oxidation cycles for the complete oxidation of caprylic acid.
Problem 58a
Lignoceric acid, CH3 ― (CH2)22 ― COOH, is a C24 fatty acid found in peanut oil in small amounts.
a. State the number of β oxidation cycles for the complete oxidation of lignoceric acid.
Problem 59a
Consider the complete oxidation of oleic acid, CH3 ― (CH2)7 ― CH = CH ― (CH2)7 ― COOH, which is a C18 monounsaturated fatty acid.
a. How many cycles of β oxidation are needed?
Problem 60a
Consider the complete oxidation of palmitoleic acid, CH3 ― (CH2)5 ― CH = CH ― (CH2)7 ― COOH, which is a C16 monounsaturated fatty acid found in animal and vegetable oils..
a. How many cycles of β oxidation are needed?
Problem 63
What are some conditions that characterize ketosis?
Problem 65a
Draw the condensed structural formula for the α-keto acid produced from each of the following in transamination:
a.
Problem 67
Why does the body convert NH4+ to urea?
Problem 68
Draw the condensed structural formula for urea.
Problem 69c
What metabolic substrate(s) are produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids?
c. tyrosine
Problem 70b
What metabolic substrate(s) are produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids?
b. asparagine
Problem 72
Draw the condensed structural formulas for the products of the reaction of aspartate and α-ketoglutarate which is catalyzed by aspartate transaminase (AST).
Problem 74a
Arachidic acid is a C20 fatty acid found in peanut and fish oils.
a. How many cycles of β oxidation are needed for the complete oxidation of arachidic acid?
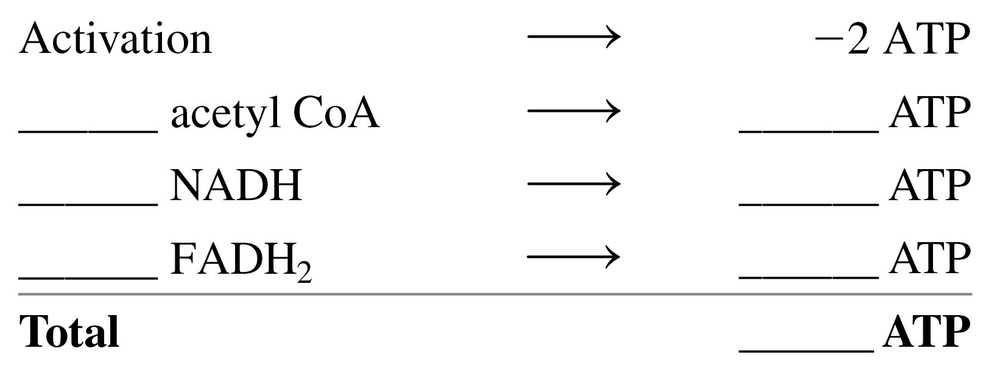
Problem 74c
Arachidic acid is a C20 fatty acid found in peanut and fish oils.
c. Calculate the total ATP yield from the complete β oxidation of arachidic acid by completing the following:
Problem 75d
Identify the type of food as carbohydrate, fat, or protein that gives each of the following digestion products:
d. glycerol
Problem 75e
Identify the type of food as carbohydrate, fat, or protein that gives each of the following digestion products:
e. amino acids
Problem 76a
Identify each of the following as a six-carbon or a three-carbon compound and arrange them in the order in which they occur in glycolysis:
a. 3-phosphoglycerate
Problem 83
When is pyruvate converted to lactate in the body?
Problem 84
When pyruvate is used to form acetyl CoA, the product has only two carbon atoms. What happened to the third carbon?
Problem 87
If there are no reactions in the citric acid cycle that use oxygen, O2, why does the cycle operate only in aerobic conditions?
Problem 89
In the chemiosmotic model, how is energy provided to synthesize ATP?
Problem 92a
What metabolic substrate(s) can be produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids?
a. histidine
Problem 92d
What metabolic substrate(s) can be produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids?
d. phenylalanine
Problem 93b
One cell at work may break down 2 million (2 000 000) ATP molecules in one second. Some researchers estimate that the human body has about 1013 cells.
b. If ATP has a molar mass of 507 g/mole, how many grams of ATP are hydrolyzed in one day?
Problem 94f
State if each of the following processes release or require ATP:
f. first six reactions of glycolysis
Problem 94g
State if each of the following processes release or require ATP:
g. activation of a fatty acid
Problem 95d
Match the following ATP yields to reactions a to g:
1.5 ATP 2.5 ATP 7 ATP 10 ATP
12 ATP 32 ATP 36 ATP
d. Acetyl CoA goes through one turn of the citric acid cycle.
Problem 95f
Match the following ATP yields to reactions a to g:
1.5 ATP 2.5 ATP 7 ATP 10 ATP
12 ATP 32 ATP 36 ATP
f. NADH + H+ is oxidized to NAD+.