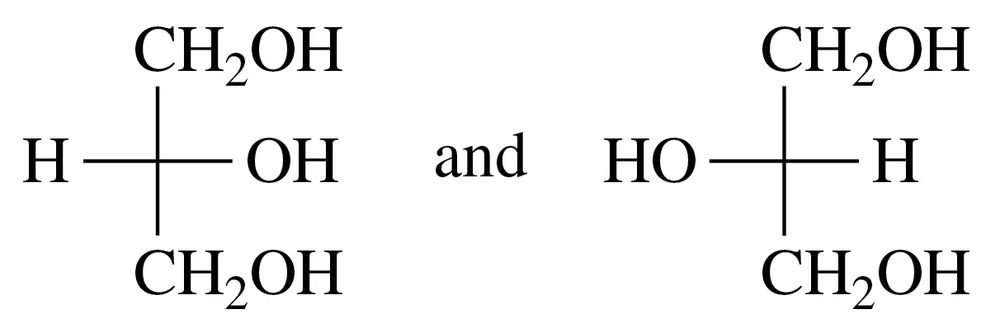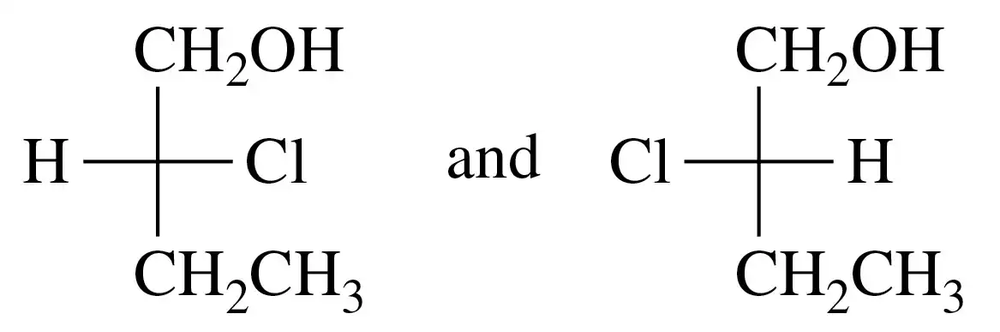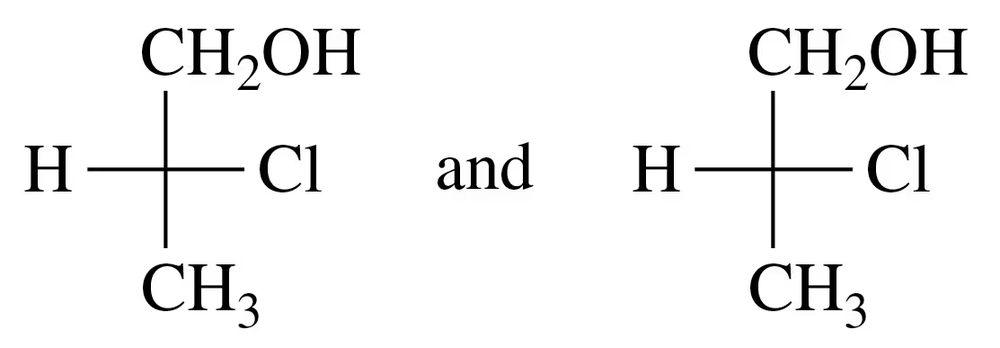Back
BackProblem 49c
Give the name of one or more polysaccharides that matches each of the following descriptions:
c. contains only α(1→4)-glycosidic bonds
Problem 50b
Give the name of one or more polysaccharides that matches each of the following descriptions:
b. contains only ß(1→4)-glycosidic bonds
Problem 50d
Give the name of one or more polysaccharides that matches each of the following descriptions:
d. produces maltose during digestion
Problem 55a
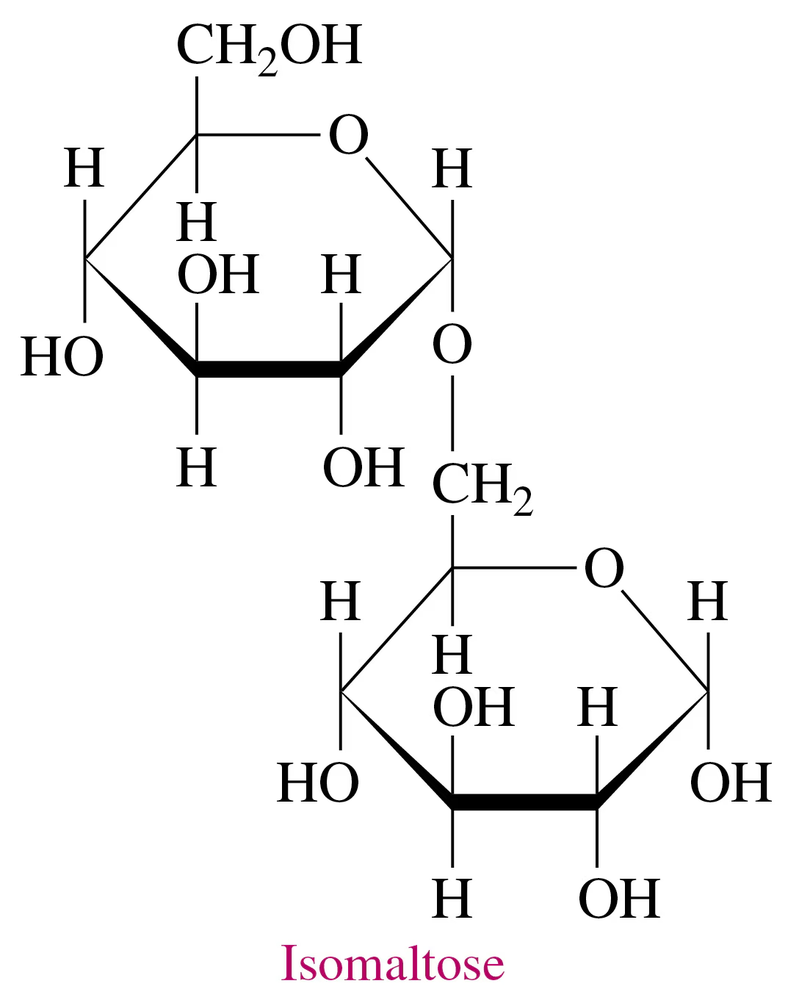
Isomaltose, obtained from the breakdown of starch, has the following Haworth structure:
a. Is isomaltose a mono-, di-, or polysaccharide?
Problem 55b
Isomaltose, obtained from the breakdown of starch, has the following Haworth structure:
b. What are the monosaccharides in isomaltose?
Problem 55d
Isomaltose, obtained from the breakdown of starch, has the following Haworth structure:
d. Is this the α or β isomer of isomaltose?
Problem 57a
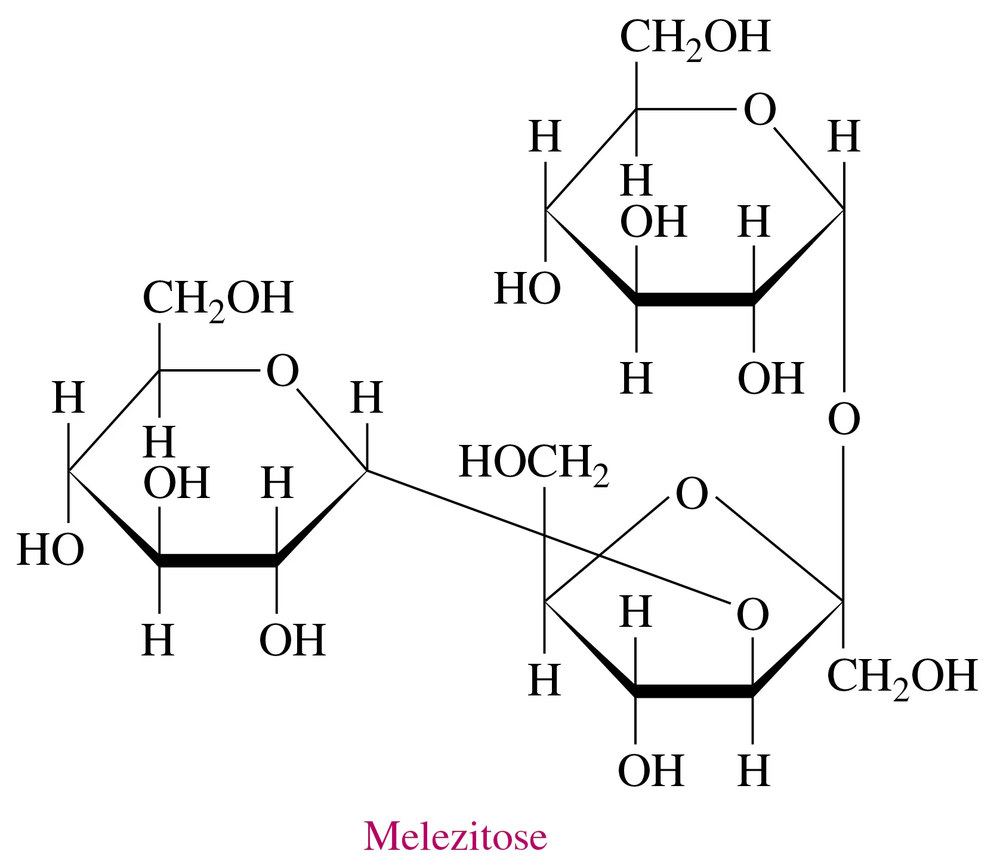
Melezitose, a carbohydrate secreted by insects, has the following Haworth structure:
a. Is melezitose a mono-, di-, or trisaccharide?
Problem 57b
Melezitose, a carbohydrate secreted by insects, has the following Haworth structure:
b. What monosaccharides are present in melezitose?
Problem 57c
Melezitose, a carbohydrate secreted by insects, has the following Haworth structure:
c. Is melezitose a reducing sugar?
Problem 59a
What are the disaccharides and polysaccharides present in each of the following?
a. <IMAGE>
Problem 60a
What are the disaccharides and polysaccharides present in each of the following?
a. <IMAGE>
Problem 63a
Identify each of the following pairs of Fischer projections as enantiomers or identical compounds:
a.
Problem 64a
Identify each of the following pairs of Fischer projections as enantiomers or identical compounds:
a.
Problem 64c
Identify each of the following pairs of Fischer projections as enantiomers or identical compounds:
c.
Problem 65
What are the differences in the Fischer projections of d-fructose and d-galactose?
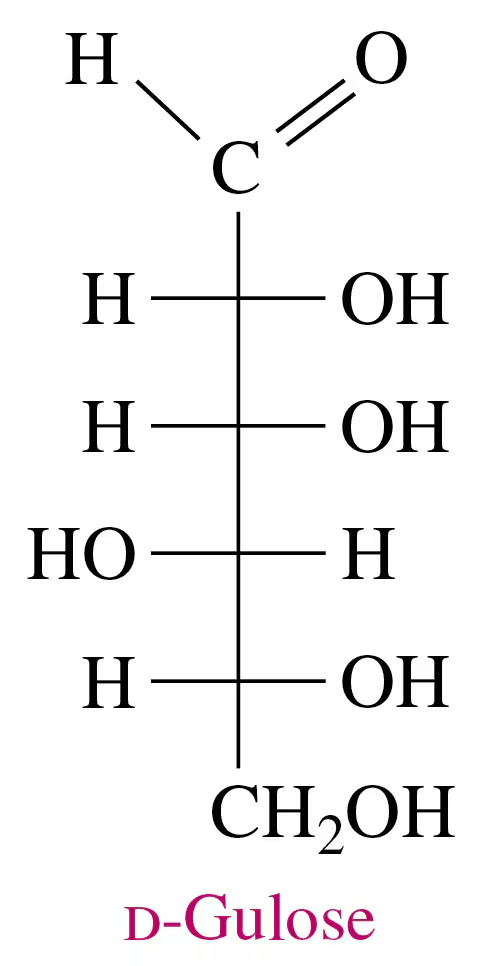
Problem 69a
The sugar d-gulose is a sweet-tasting syrup.
a. Draw the Fischer projection for L-gulose.
Problem 69b
The sugar d-gulose is a sweet-tasting syrup.
b. Draw the Haworth structures for α− and β-D-gulose.
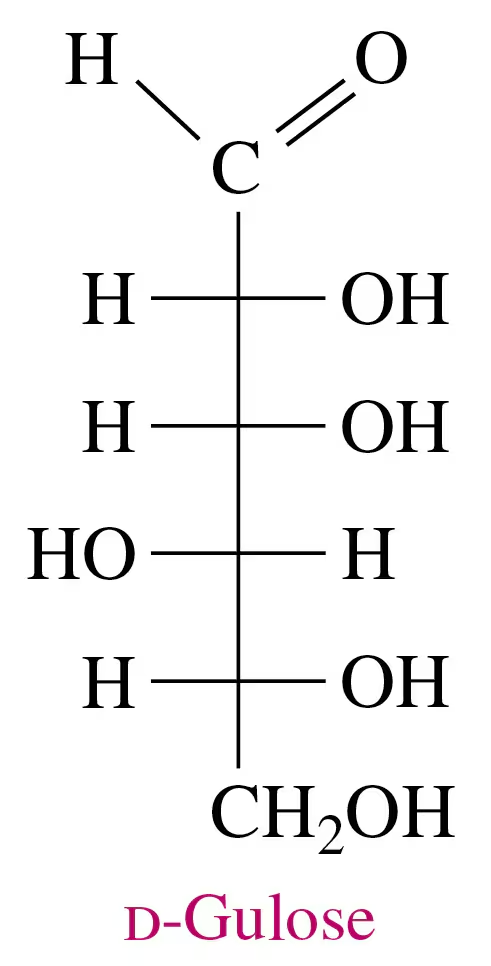
Problem 70a
Use the Fischer projection for d-gulose in problem 13.69 to answer each of the following:
a. Draw the Fischer projection and name the product formed by the reduction of D-gulose.
Problem 70b
Use the Fischer projection for D-gulose in problem 13.69 to answer each of the following:
b. Draw the Fischer projection and name the product formed by the oxidation of D-gulose.
Problem 72
D-Erythritol is 70% as sweet as sucrose and contains only hydroxyl functional groups. When d-erythritol is oxidized it forms D-erythrose. Draw the Fischer projection for D-erythritol.
Problem 73
If α−galactose is dissolved in water, β−galactose is eventually present. Explain how this occurs.
Problem 75
α−Cellobiose is a disaccharide obtained from the hydrolysis of cellulose. It is quite similar to maltose except it has a β(1→4)−glycosidic bond. Draw the Haworth structure for α−cellobiose.
Problem 76
The disaccharide trehalose found in mushrooms is composed of two α-D-glucose molecules joined by an α(1→1)−glycosidic bond. Draw the Haworth structure for trehalose.
Problem 77b
Gentiobiose is found in saffron.
b. Is gentiobiose a reducing sugar? Explain.