Back
BackProblem 42a
What is meant by the term base pairing?
Problem 44
What does it mean to speak of bases as being complementary?
Problem 45
The DNA from sea urchins contains about 32% A and about 18% G. What percentages of T and C would you expect in sea urchin DNA? Explain.
Problem 46
If a double-stranded DNA molecule is 22% G, what is the percentage of A, T, and C? Explain.
Problem 47
How are replication, transcription, and translation similar? How are they different?
Problem 51
Rank the following in order of size: tRNA, DNA, mRNA.
Problem 56
What is an anticodon, and on what kind of nucleic acid is it found?
Problem 57a
Which amino acid(s) have the most codons?
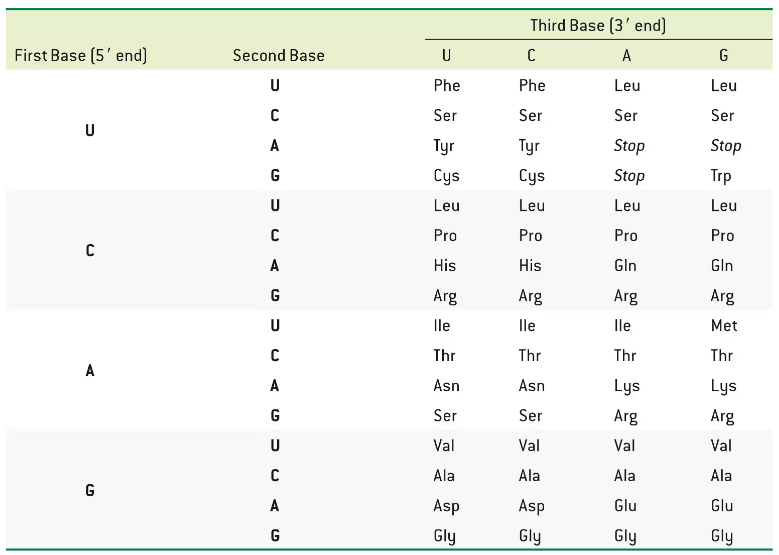
Problem 58a
Look at Table 26.3 and find codons for the following amino acids:
a. Val
Problem 62
If the sequence T-A-C-C-C-T appears on the informational strand of DNA, what sequence appears opposite it on the template strand? Label your answer with 3′ and 5′ ends.
Problem 65
What tetrapeptide is synthesized from the informational DNA sequence G-T-C-A-G-T-A-C-G-T-T-A?
Problem 68
What is the general shape and structure of a tRNA molecule?
Problem 69
There are different tRNAs for each amino acid. What is one major way to differentiate among the tRNAs for each amino acid?
Problem 71
Insulin is synthesized as preproinsulin, which has 81 amino acids. How many heterocyclic bases must be present in the informational DNA strand to code for preproinsulin (assuming no introns are present)?
Problem 74
Suppose that 22% of the nucleotides of a DNA molecule are deoxyadenosine and during replication the relative amounts of available deoxynucleoside triphosphates are 22% dATP, 22% dCTP, 28% dGTP, and 28% dTTP. What deoxynucleoside triphosphate is limiting to the replication? Explain.