Back
BackProblem 7a
Does entropy increase or decrease in the following processes?
a. Polymeric complex carbohydrates are metabolized by the body, converted into smaller simple sugars.
Problem 7c
Does entropy increase or decrease in the following processes?
c. 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g)
Problem 12a
Do the following reactions favor reactants or products at equilibrium? Give relative concentrations at equilibrium.
a. Sucrose(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ Glucose(aq) + Fructose(aq) K = 1.4 × 105
Problem 12c
Do the following reactions favor reactants or products at equilibrium? Give relative concentrations at equilibrium.
c. Fe2O3(s) + 3 CO(g) ⇌ 2 Fe(s) + 3 CO2(g) K (at 727 °C) = 24.2
Problem 14a
The following diagrams represent two similar reactions that have achieved equilibrium:
<IMAGE>
a. Write the expression for the equilibrium constant for each reaction.
Problem 14b
The following diagrams represent two similar reactions that have achieved equilibrium:
<IMAGE>
b. Calculate the value for the equilibrium constant for each reaction.
Problem 15
Is the yield of SO3 at equilibrium favored by a higher or lower pressure? By a higher or lower temperature?
2 SO2(g) + O2 ⇌ 2 SO3(g) ∆H = -47 kcal/mol
Problem 16a
What effect do the listed changes have on the position of the equilibrium in the reaction of carbon with hydrogen?
C(s) + 2 H2(g) ⇌ CH4(g) ∆H = -18 kcal/mol (-75kJ/mol)
a. Increasing temperature
Problem 16b
What effect do the listed changes have on the position of the equilibrium in the reaction of carbon with hydrogen?
C(s) + 2 H2(g) ⇌ CH4(g) ∆H = -18 kcal/mol (-75kJ/mol)
b. Increasing pressure by decreasing volume
Problem 16c
What effect do the listed changes have on the position of the equilibrium in the reaction of carbon with hydrogen?
C(s) + 2 H2(g) ⇌ CH4(g) ∆H = -18 kcal/mol (-75kJ/mol)
c. Allowing CH4 to escape continuously from the reaction vessel
Problem 21b
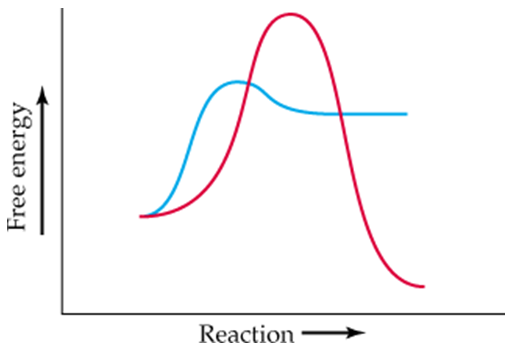
Two curves are shown in the following energy diagram:
b. Which curve represents the spontaneous reaction, and which the nonspontaneous?
Problem 22a
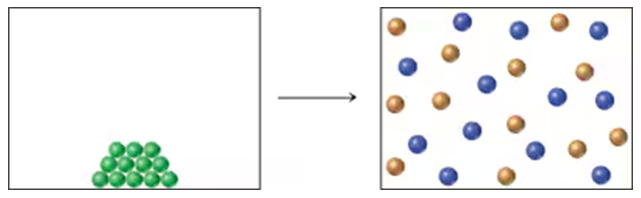
The following diagram portrays a reaction of the type A(s) → B(g) + C(g), where the different-colored spheres represent different molecular structures. Assume that the reaction has ∆H = +9.1 kcal/mol (+38.1 kJ/mol).
a. What is the sign of ∆S for the reaction?
Problem 22b
The following diagram portrays a reaction of the type A(s) → B(g) + C(g), where the different-colored spheres represent different molecular structures. Assume that the reaction has ∆H = +9.1 kcal/mol (+38.1 kJ/mol).
b. Is the reaction likely to be spontaneous at all temperatures, nonspontaneous at all temperatures, or spontaneous at some but nonspontaneous at others?
Problem 23
Is the total enthalpy (H) of the reactants for an endothermic reaction greater than or less than the total enthalpy of the products?
Problem 25a
The vaporization of Br2 from the liquid to the gas state requires 7.4 kcal/mol (31.0 kJ/mol).
a. What is the sign of ∆H for this process? Write a reaction showing heat as a product or reactant.
Problem 25c
The vaporization of Br2 from the liquid to the gas state requires 7.4 kcal/mol (31.0 kJ/mol).
c. How many kilojoules are needed to evaporate 82 g of Br2?
- Converting liquid water to solid ice releases 1.44 kcal/mol (6.02 kJ/mol). How many kilocalories are released by freezing 32 g of H2O?
Problem 26
Problem 27b
Acetylene (H–C≡C–H) is the fuel used in welding torches.
b. Estimate ∆H for this reaction (in kJ/mol) using the bond energies listed in Table 7.1.
Problem 28b
Nitrogen in air reacts at high temperatures to form NO2 according to the following reaction: N2 + 2 O2 → 2 NO2
b. Estimate ∆H for this reaction (in kcal and kJ) using the bond energies from Table 7.1.
Problem 29a
Glucose, also known as "blood sugar" when measured in blood, has the formula C6H12O6.
a. Write the equation for the combustion of glucose with O2 to give CO2 and H2O.
Problem 29c
Glucose, also known as "blood sugar" when measured in blood, has the formula C6H12O6.
c. What is the minimum amount of energy (in kJ) a plant must absorb to produce 15.0 g of glucose?
Problem 31
Which of the following processes results in an increase in entropy of the system?
a. A drop of ink spreading out when it is placed in water
b. Steam condensing into drops on windows
c. Constructing a building from loose bricks
Problem 32a
For each of the following processes, specify whether entropy increases or decreases. Explain each of your answers.
a. Assembling a jigsaw puzzle
Problem 33
What two factors affect the spontaneity of a reaction?
Problem 34
What is the difference between an exothermic reaction and an exergonic reaction?
Problem 36
Under what conditions might a reaction be endothermic but exergonic? Explain.
Problem 37b
For the reaction
b. Does entropy increase or decrease in this process?
Problem 38a
For the reaction 2 Hg(l) + O2(g) → 2 HgO(s), ∆H = –43 kcal/mol (–180 kJ/mol).
a. Does entropy increase or decrease in this process? Explain.
Problem 38b
For the reaction 2 Hg(l) + O2(g) → 2 HgO(s), ∆H = –43 kcal/mol (–180 kJ/mol).
b. Under what conditions would you expect this process to be spontaneous?
Problem 40a
The following reaction is used in the industrial synthesis of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) polymer:
Cl2(g) + H2C=CH2(g) → ClCH2CH2Cl(l) ∆H = –52 kcal/mol (–218 kJ/mol)
a. Is ∆S positive or negative for this process?