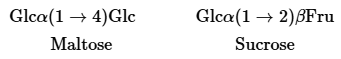Back
BackProblem 47a
Explain whether the following blood types could be donated to a person with type B blood:
(a) A
Problem 49
How is the polysaccharide heparin different from the glucose polysaccharides?
Problem 51
Write the molecular formula for a carbohydrate containing three carbons.
Problem 52
What would be the molecular formula of a monosaccharide characterized as an aldopentose?
Problem 53
Explain the difference between an oligosaccharide and a polysaccharide.
Problem 54
Explain the difference between an aldose and a ketose.
Problem 55
Describe the properties of soluble fiber.
Problem 57
Name the functional groups present in aldoses.
Problem 63a
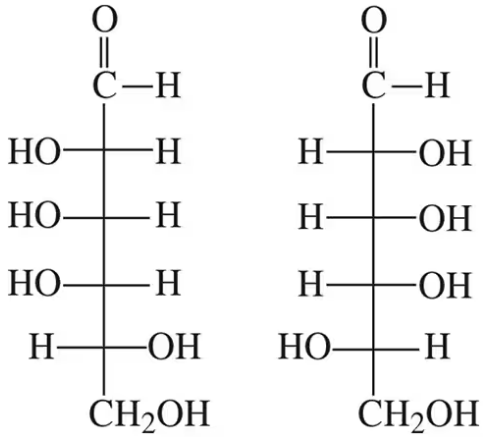
How are the following pairs of carbohydrates, shown in a Fischer projection, related to each other? Are they structural isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or epimers? Identify each as the D- or L-isomer.
(a)
Problem 63b
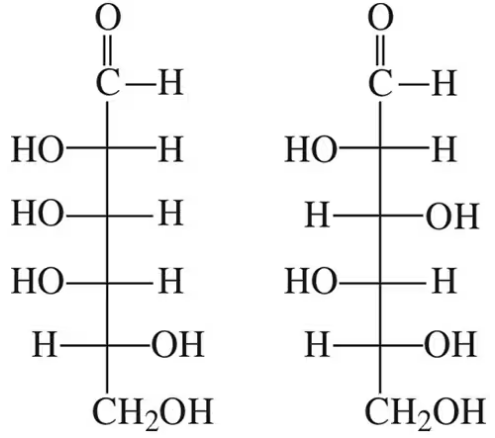
How are the following pairs of carbohydrates, shown in a Fischer projection, related to each other? Are they structural isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or epimers? Identify each as the D- or L-isomer.
(b)
Problem 64a
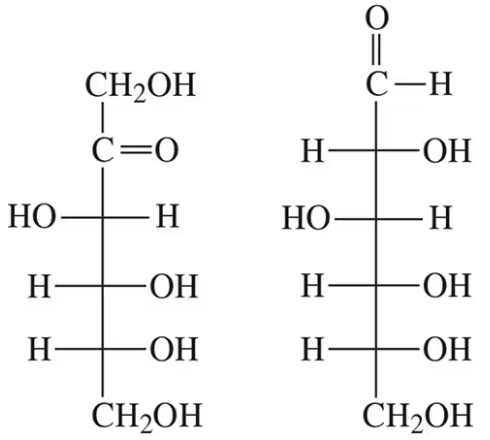
How are the following pairs of carbohydrates, shown in a Fischer projection, related to each other? Are they structural isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or epimers?
(a)
Problem 65
Draw the Fischer projection of the C3 epimer of D-glucose. Compare your structure with those in Table 6.1 and give the name of this compound.
Problem 67a
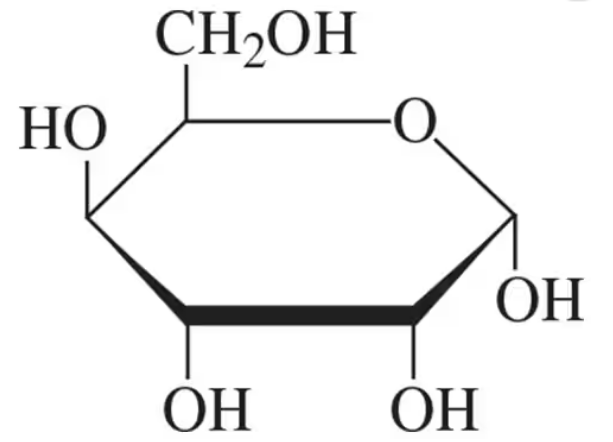
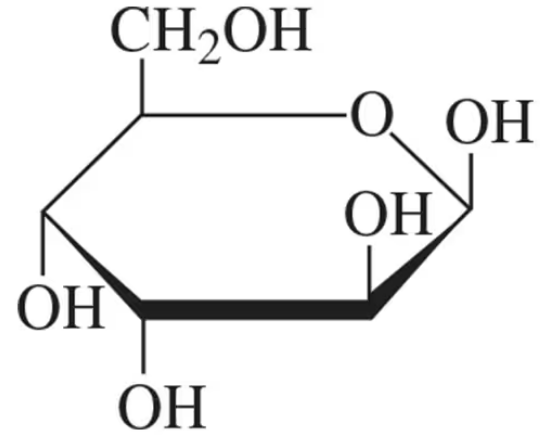
Identify the following carbohydrates as the ⍺ or β anomer:
(a)
Problem 68b
Identify the following carbohydrates as the ⍺ or β anomer:
(b)
Problem 71
Draw the Fischer projection of the product of the oxidation of D-galactose at C1.
Problem 73
Draw the Fischer projection of the product of reduction reaction of D-galactose at C1.
Problem 75a
Will the following carbohydrates produce a positive Benedict's test?
a. D-glucose
Problem 75b
Will the following carbohydrates produce a positive Benedict’s test?
b. lactose
Problem 77
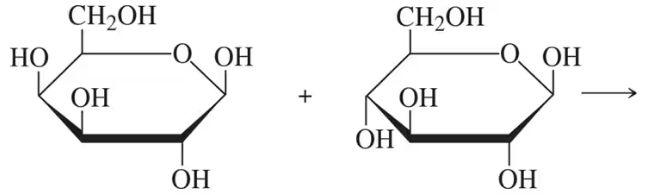
Draw the product of the following 1→4 condensation and name the glycosidic bond:
Problem 79
Isomaltose, a disaccharide formed during caramelization in cooking, contains two glucose units bonded ⍺(1→6). Draw the structure of isomaltose.
Problem 80
The glycosidic bond in a disaccharide was determined to be α(1→6). Hydrolysis of the disaccharide produced one galactose and one fructose. Draw the structure of the disaccharide.
Problem 82
Our bodies cannot digest cellulose because we lack the enzyme cellulase. Why is cellulose an important part of a healthy diet if we cannot digest it?
Problem 83
The shell of a shrimp is composed of chitin. If you eat a boiled shrimp without removing the shell, will your body break the shell down into its component sugars? Explain. (Hint: Compare chitin’s structure to that of amylose and cellulose.)
Problem 84
Glycogen and amylopectin are both branched polymers of glucose. Read the descriptions of each in Section 6.6. Which molecule has a more compact structure? Explain.
Problem 87
On an exam, a student was asked to draw the Fischer projection of L-glucose, but he had only memorized the structure of D-glucose. He wrote the structure of D-glucose and switched the hydroxyl group on C5 from the right to the left. Was his answer correct? If not, what is the name of the aldose that he drew?
Problem 88
Carbohydrates are abbreviated using a three-letter abbreviation followed by their glycosidic bond type. For example, maltose and sucrose can be written respectively as
Provide the structure for the O-type blood carbohydrate set given the following abbreviation:
L-Fucα (1→2) Galß(1→4)GlcNAc
Problem 89a
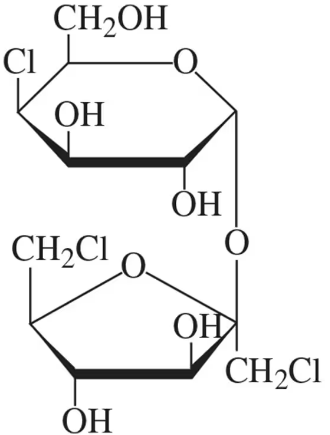
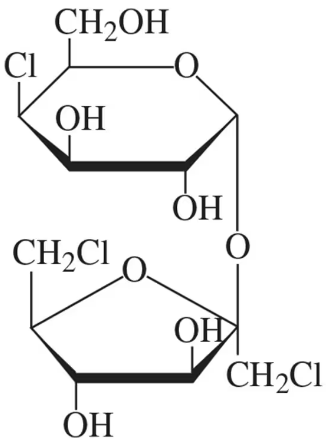
The structure of sucralose, found in the artificial sweetener Splenda, is shown in the figure. It consists of a chlorinated disaccharide made up of galactose and fructose. In its structure shown,
(a) identify the galactose unit and the fructose unit.
Problem 89b
The structure of sucralose, found in the artificial sweetener Splenda, is shown in the figure. It consists of a chlorinated disaccharide made up of galactose and fructose. In its structure shown, (b) identify the type of glycosidic bond present.
Problem 90
Which of the components in starch is more likely to be broken down more quickly in plants, amylose or amylopectin? Why?
Problem 91
How much energy is produced if a person eats 50 g of digestible carbohydrate (not fiber) in a day? In this case, what percent of a 2200 Calorie diet would be digestible carbohydrate? Recall that carbohydrates provide four Calories of energy per gram consumed.