Textbook Question
Explain why diabetics produce high levels of ketone bodies.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

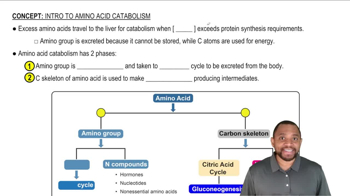
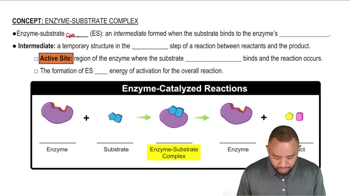
Explain why diabetics produce high levels of ketone bodies.
Name the metabolic substrate(s) that can be produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids:
a. alanine
Name the metabolic substrate(s) that can be produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids:
c. valine
Name the location in the cell where the following catabolic processes take place:
a. glycolysis
Name the location in the cell where the following catabolic processes take place:
b. citric acid cycle
Name the location in the cell where the following catabolic processes take place:
c. β oxidation