Textbook Question
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
List the names and abbreviations of the four nucleotides in RNA.
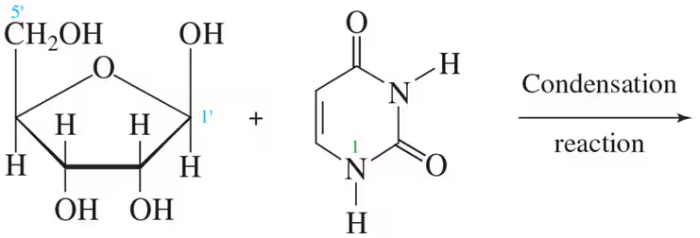
Provide the products for each of the following condensation reactions:
a.
Provide the products for each of the following condensation reactions:
b.
What is the name of the bond that joins nucleotides in a nucleic acid?
Describe the differences in the two ends of a nucleic acid.