Textbook Question
Glycine has the zwitterion structure shown. Draw the structure and give the net charge of glycine that will predominate at the indicated pH values (pI = 6.0).
a. pH 1.5

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Glycine has the zwitterion structure shown. Draw the structure and give the net charge of glycine that will predominate at the indicated pH values (pI = 6.0).
a. pH 1.5
Glycine has the zwitterion structure shown. Draw the structure and give the net charge of glycine that will predominate at the indicated pH values (pI = 6.0).
b. pH 12.0
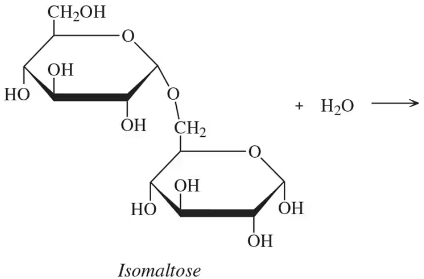
Write the products for the following condensation or hydrolysis reactions:
a.
Consider the following tripeptide:
a. Circle the N-terminal amino acid, and give its name. Draw a square around the C-terminal amino acid, and give its name.
Consider the following tripeptide:
b. Give the one-letter and three-letter abbreviations of this tripeptide.
Draw the structural formula for each of the following peptides:
b. KCG