Consider the amino acids glycine, proline, and lysine.
b. Using three-letter abbreviations for the amino acids, give the sequence for each of the possible tripeptides.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Consider the amino acids glycine, proline, and lysine.
b. Using three-letter abbreviations for the amino acids, give the sequence for each of the possible tripeptides.
Indicate whether each of the following describes a competitive or a noncompetitive inhibitor.
e. Adding more substrate to the reaction restores the enzyme activity.
Give the name and three-letter abbreviation for the amino acid described by each of the following:
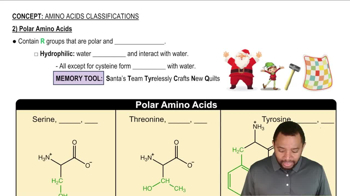
a. the nonpolar amino acid with a sulfur atom in its side chain
Give the name and three-letter abbreviation for the amino acid described by each of the following:
a. the polar amino acid with a benzene ring in its side chain
Aspartame, which is commonly known as NutraSweet™, contains the following dipeptide:
d. Draw the structure of the isomer of this dipeptide where the C-terminal and N-terminal amino acids are switched.
Draw the structure of the possible dipeptides formed from one alanine combining with one cysteine.