Give the three-letter and one-letter abbreviations and identify the functional group in the side chain for each amino acid in Problem 10.1.
a. alanine
b. lysine
c. tryptophan
d. aspartate

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

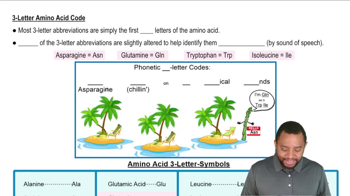

Give the three-letter and one-letter abbreviations and identify the functional group in the side chain for each amino acid in Problem 10.1.
a. alanine
b. lysine
c. tryptophan
d. aspartate
Draw the structure for each of the following amino acids and put an asterisk (*) next to any chiral carbon centers in your structure:
c. methionine
Classify each amino acid in Problem 10.4 as polar (neutral, acidic, or basic) or nonpolar and as hydrophobic or hydrophilic.
a. leucine
b. glutamate
c. methionine
d. threonine
Draw the structure for the amino acid represented by each of the following abbreviations:
d. Ile
Draw the structure for the amino acid represented by each of the following abbreviations:
c. Val
Draw the structure for the amino acid represented by each of the following abbreviations:
d. Y