Back
BackProblem 4
Outline the events that occur during initiation of translation in E. coli.
Problem 5a
A portion of a DNA template strand has the base sequence
5′-...ACGCGATGCGTGATGTATAGAGCT...-3′
Identify the sequence and polarity of the mRNA transcribed from this fragmentary template-strand sequence.
Problem 5b
A portion of a DNA template strand has the base sequence
5′-...ACGCGATGCGTGATGTATAGAGCT...-3′
Assume the mRNA is written in the correct reading frame. Determine the amino acid sequence encoded by this fragment. Identify the N- and C-terminal directions of the polypeptide.
Problem 5c
A portion of a DNA template strand has the base sequence
5′-...ACGCGATGCGTGATGTATAGAGCT...-3′
Which is the third amino acid added to the polypeptide chain?
Problem 6
Describe three features of tRNA molecules that lead to their correct charging by tRNA synthetase enzymes.
Problem 7a
Identify the amino acid carried by tRNAs with the following anticodon sequences.
5′-UAG-3′
Problem 7b
Identify the amino acid carried by tRNAs with the following anticodon sequences.
5′-AAA-3′
Problem 7c
Identify the amino acid carried by tRNAs with the following anticodon sequences.
5′-CUC-3′
Problem 7d
Identify the amino acid carried by tRNAs with the following anticodon sequences.
5′-AUG-3′
Problem 7e
Identify the amino acid carried by tRNAs with the following anticodon sequences.
5′-GAU-3′
Problem 8
For each of the anticodon sequences given in the previous problem, identify the other codon sequence to which it could potentially pair using third base wobble.
Problem 9
What is the role of codons UAA, UGA, and UAG in translation? What events occur when one of these codons appears at the A site of the ribosome?
Problem 10
Compare and contrast the composition and structure of bacterial and eukaryotic ribosomes, identifying at least three features that are the same and three features that are unique to each type of ribosome.
Problem 11a
Consider translation of the following mRNA sequence:
5′-...AUGCAGAUCCAUGCCUAUUGA...-3′
Diagram translation at the moment the fourth amino acid is added to the polypeptide chain. Show the ribosome; label its A, P, and E sites; show its direction of movement; and indicate the position and anticodon triplet sequence of tRNAs that are currently interacting with mRNA codons.
Problem 11b
Consider translation of the following mRNA sequence:
5′-...AUGCAGAUCCAUGCCUAUUGA...-3′
What is the anticodon triplet sequence of the next tRNA to interact with mRNA?
Problem 11c
Consider translation of the following mRNA sequence:
5′-...AUGCAGAUCCAUGCCUAUUGA...-3′
What events occur to permit the next tRNA to interact with mRNA?
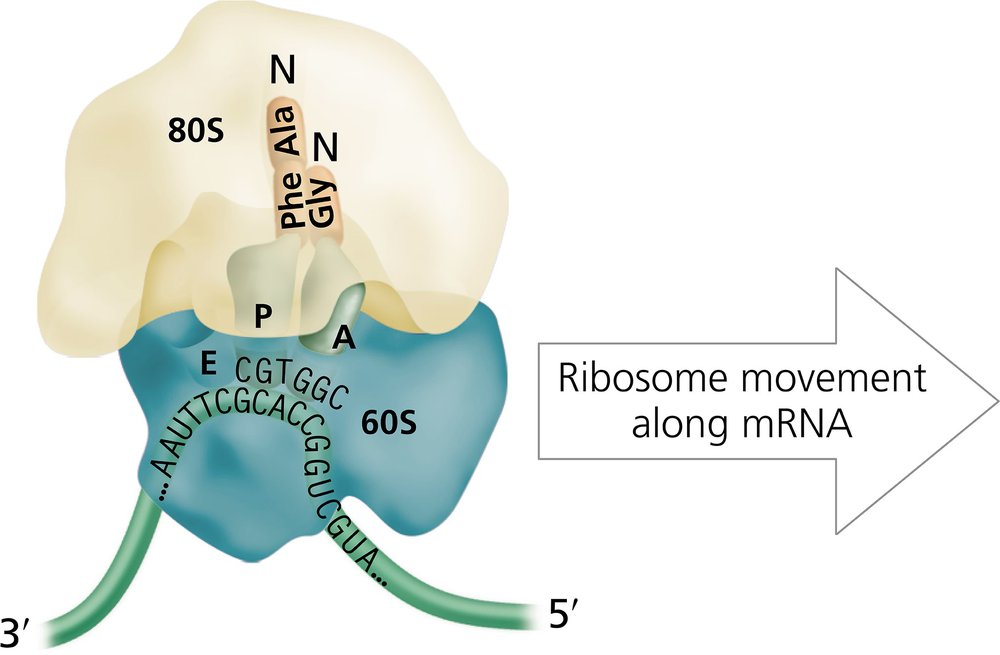
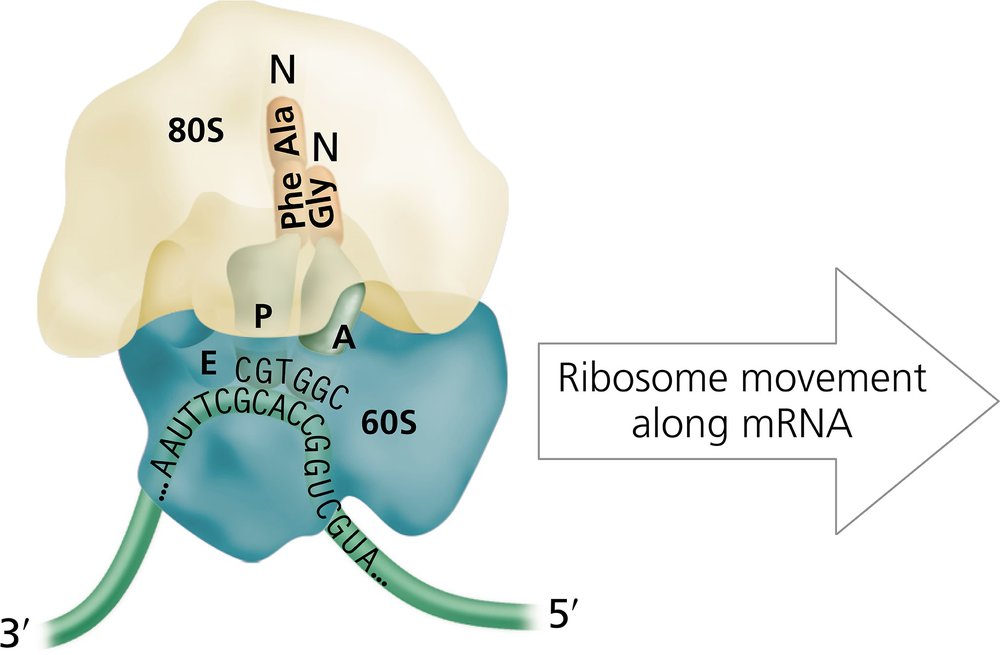
Problem 12a
The diagram of a eukaryotic ribosome shown below contains several errors.
Examine the diagram carefully, and identify each error.
Problem 12b
The diagram of a eukaryotic ribosome shown below contains several errors.
Redraw the diagram, and correct each error using the mRNA sequence shown.
Problem 13a
Third-base wobble allows some tRNAs to recognize more than one mRNA codon. Based on this chapter's discussion of wobble, what is the minimal number of tRNA molecules necessary to recognize the following amino acids?
Leucine
Problem 13b
Third-base wobble allows some tRNAs to recognize more than one mRNA codon. Based on this chapter's discussion of wobble, what is the minimal number of tRNA molecules necessary to recognize the following amino acids?
Arginine
Problem 13c
Third-base wobble allows some tRNAs to recognize more than one mRNA codon. Based on this chapter's discussion of wobble, what is the minimal number of tRNA molecules necessary to recognize the following amino acids?
Isoleucine
Problem 13d
Third-base wobble allows some tRNAs to recognize more than one mRNA codon. Based on this chapter's discussion of wobble, what is the minimal number of tRNA molecules necessary to recognize the following amino acids?
Lysine
Problem 14
The genetic code contains 61 codons to specify the 20 common amino acids. Many organisms carry fewer than 61 different tRNA genes in their genomes. These genomes take advantage of isoaccepting tRNAs and the rules governing third-base wobble to encode fewer than 61 tRNA genes. Use these rules to calculate the minimal number of tRNA genes required to specify all 20 of the common amino acids.
Problem 15a
The three major forms of RNA (mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA) interact during translation.
Describe the role each form of RNA performs during translation.
Problem 15b
The three major forms of RNA (mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA) interact during translation.
Which of the three types of RNA might you expect to be the least stable? Why?
Problem 15c
The three major forms of RNA (mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA) interact during translation.
Which form of RNA is least stable in eukaryotes? Why is this form least stable?
Problem 15d
The three major forms of RNA (mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA) interact during translation.
Compared to the average stability of mRNA in E. coli, is mRNA in a typical human cell more stable or less stable? Why?
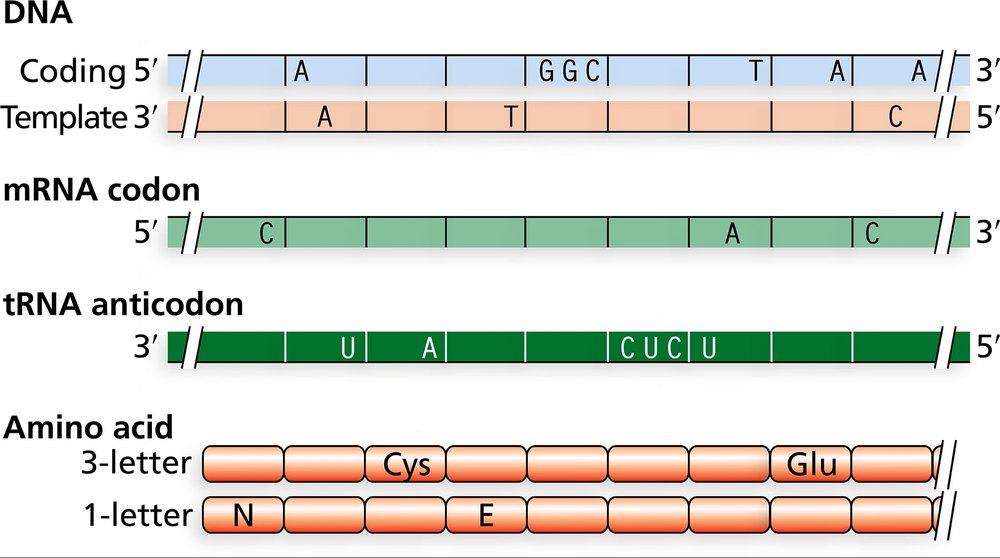
Problem 16
The accompanying figure contains sufficient information to fill in every row. Use the information provided to complete the figure.
Problem 17
The line below represents a mature eukaryotic mRNA. The accompanying list contains many sequences or structures that are part of eukaryotic mRNA. A few of the items in the list, however, are not found in eukaryotic mRNA. As accurately as you can, show the location, on the line, of the sequences or structures that belong in eukaryotic mRNA; then, separately, list the items that are not part of eukaryotic mRNA.
5′ ____________________________ 3′
a. stop codon
b. poly-A tail
c. intron
d. 3' UTR
e. promoter
f. start codon
g. AAUAAA
h. 5' UTR
i. 5' cap
j. termination sequenceProblem 18
After completing Problem 17, carefully draw a line below the mRNA to represent its polypeptide product in accurate alignment with the mRNA. Label the N-terminal and C-terminal ends of the polypeptide. Carefully draw two lines above and parallel to the mRNA, and label them 'coding strand' and 'template strand.' Locate the DNA promoter sequence. Identify the locations of the nucleotide and of a transcription termination sequence.